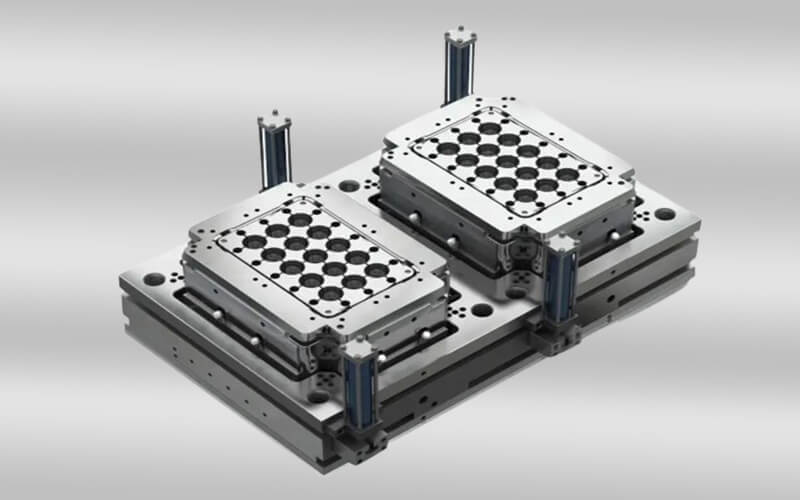
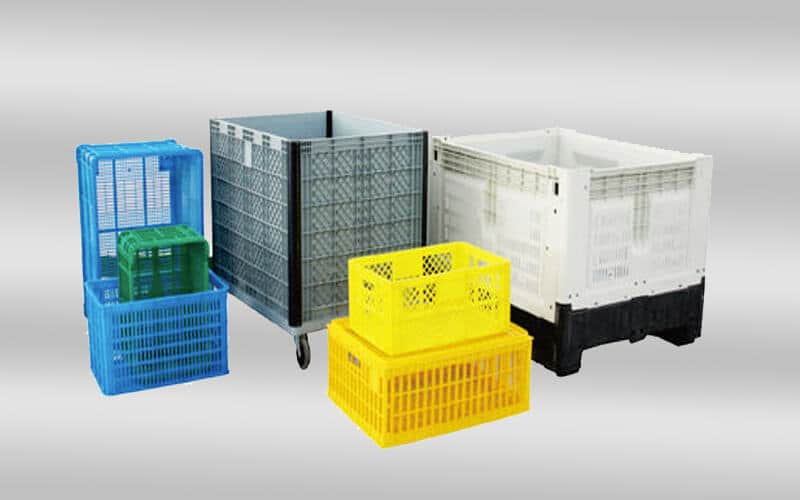
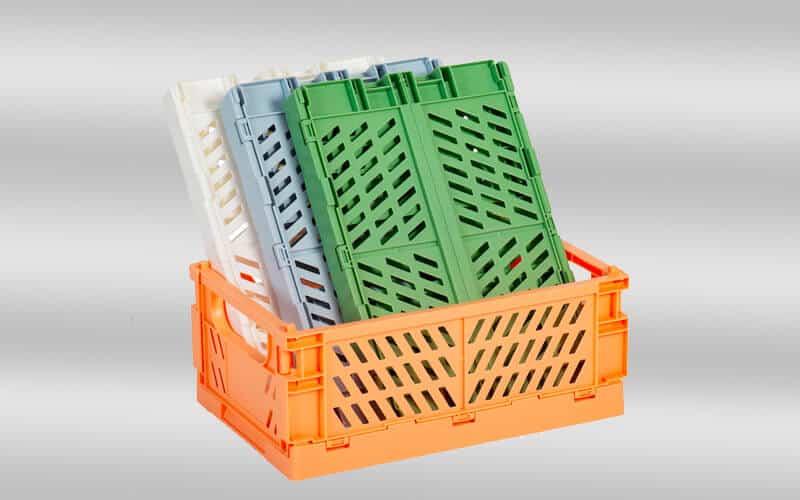
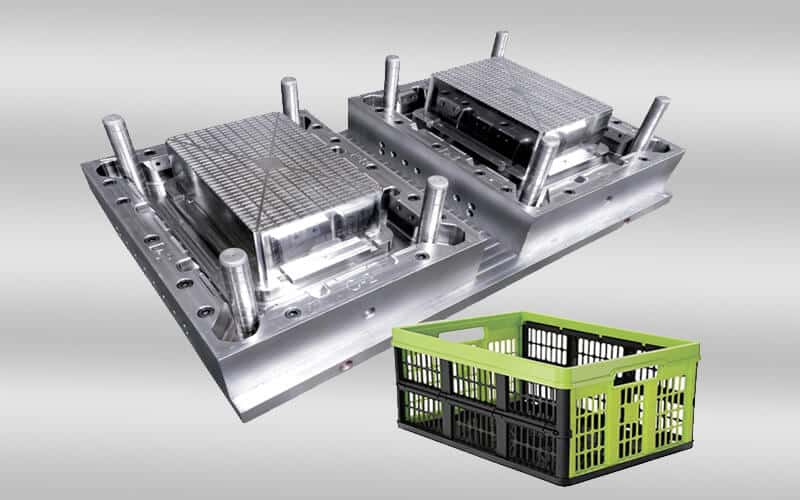
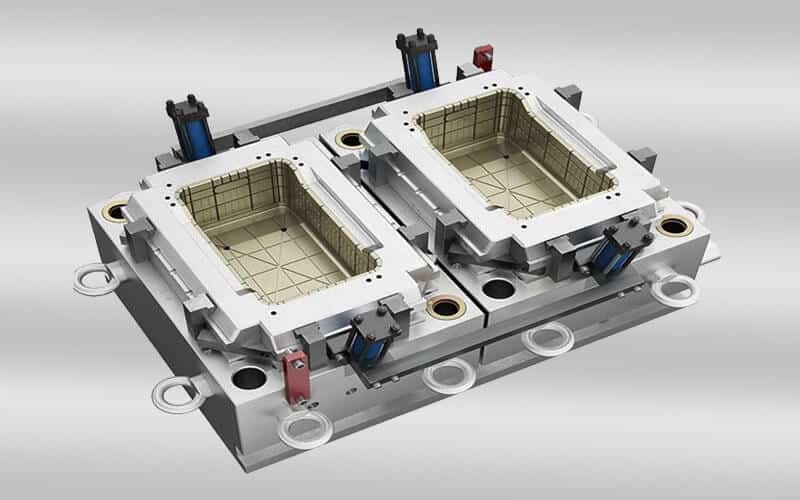
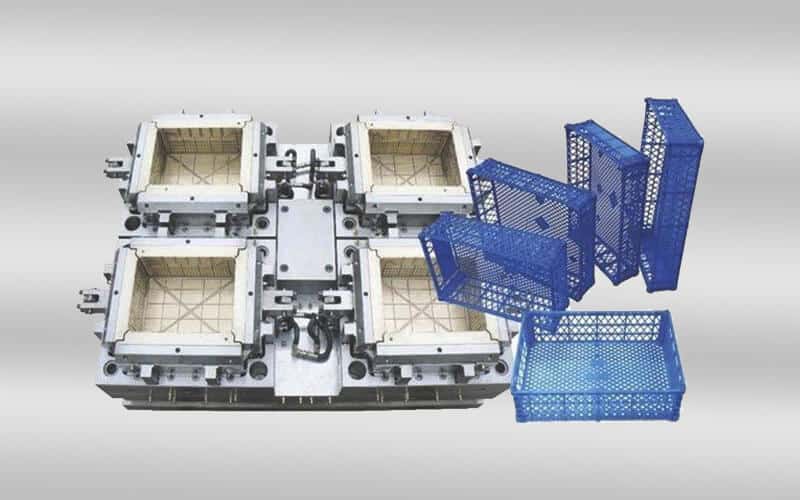
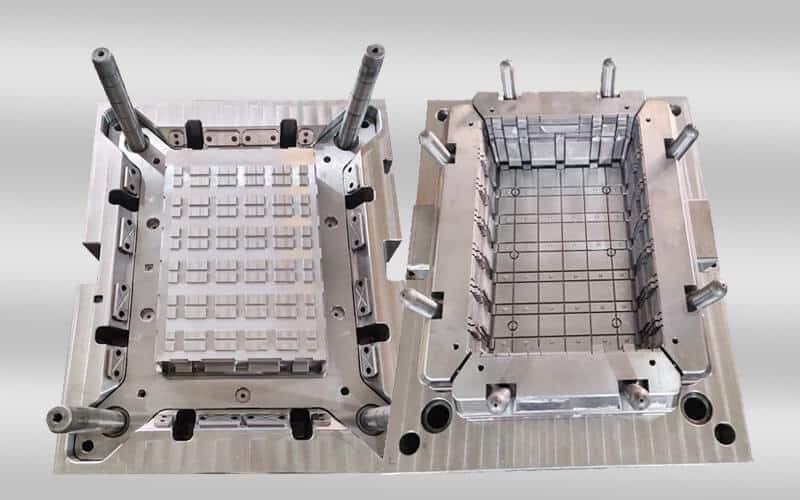
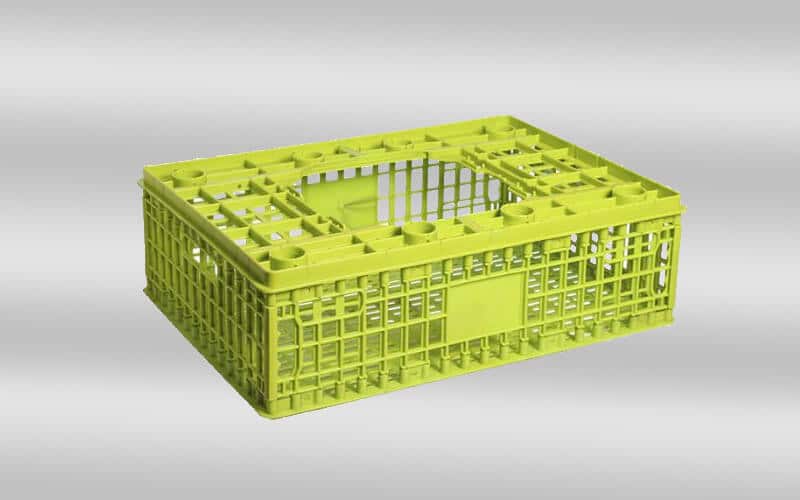
crate mold design & manufacturing in China
Whether you need professional crate mold design and manufacturing or one-stop crate molding services, YUCO MOLD can meet your requirements.
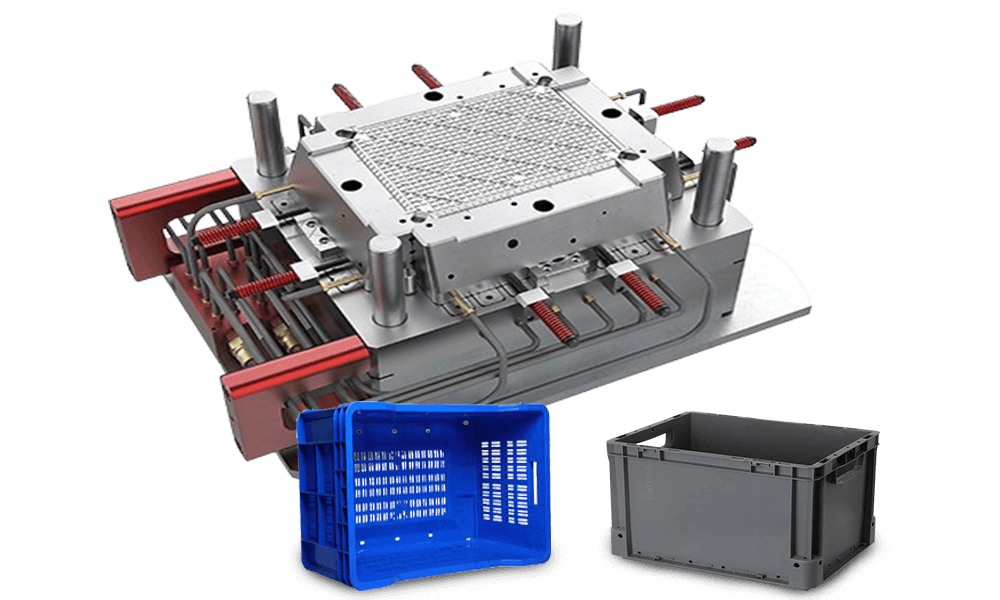
The advantages of making crate molds in YUCO
As a leading crate manufacturer in China, YUCO has unique advantages that set it apart in the global market:
- Competitive pricing: Leverage the cost-effectiveness of Chinese manufacturing without compromising quality.
- Vast manufacturing capacity: Our large-scale facilities can handle orders of any size, from small batches to large-volume production, or the production of industrial-grade large crates.
- Skilled workforce: Our team combines traditional craftsmanship with modern expertise to achieve superior results.
- Custom flexibility: We quickly adapt to your specific requirements, whether it's color customization, crate design.
Introduction to crates and crate molds
Crate mold is a precision-engineered injection mold used to shape molten plastic into a sturdy plastic crate. Plastic crate is a large container used to transport or store goods. They are popular for durability, lightness, and resistance to moisture and insects. Plastic crates come in a variety of sizes and designs and are widely used in transportation, distribution, storage, circulation processing, etc. in various industries. In factories, plastic turnover crates are often used to assemble parts. In agriculture, plastic turnover crates are used to pack potatoes, tomatoes, and other fresh vegetables. Plastic turnover crates can also be used with a variety of logistics containers and workstations, suitable for various warehouses, production sites, etc.
| Mold attributes | Parameter | |
| Mold Material | 45# / P20 / 718 / 2314 | |
| Mold cavity | 1/2/4 cavities | |
| Material Hardness | HRC28 to HRC60 | |
| Mold runner | Hot runner | |
| Material Handling | Quenching / Nitrided / Heat | |
| Mold surface | Texture / Mirror polish / Customizable | |
| Mold Base | DME / LKM / HASCO / LOCAL | |
| Mold design | 3D / 2D | |
| Product Material | PP / HDPE / PET | |
| Our Services | Mold design / Mold manufacturing / Plastic injection molding / OEM service | |
| Delivery time | 50-60 days | |
| Mold life |
|
|
Brighten up your next plastic crate mold!
We do both crate mold production and mass production of various plastic crates. Welcome to customize your own molds and products.

materials used in crate mold making and molding
The production of high-quality plastic crates relies heavily on two key materials: the metal used to make the mold itself and the plastic used in the forming process.
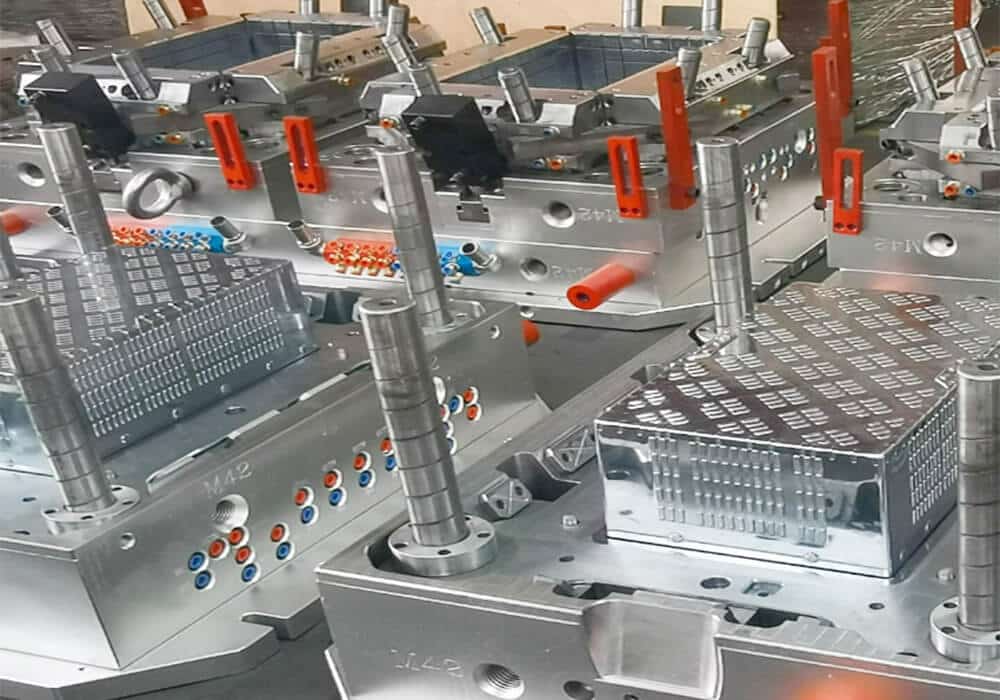
Crate molds are usually made of tool steel or aluminum to withstand the pressure and temperature of the injection molding process. It is strongly recommended that the mold steel be treated with three processes, the first tempering, the second vacuum 42-46 degree hardness treatment, and the third 48 hours of heat preservation tempering. The most common materials include:
- P20 steel
- 718H steel
- H13 steel
- 7075 aluminum
- Beryllium copper alloy
The choice of mold material depends on factors such as the expected production volume, the complexity of the crate design, and the specific molding process to be used. You must choose the right steel or material to make a durable mold component. If mold usage rate is relatively high, 45# steel is generally used, and the mold core, mold cavity, and slider are nitrided 718H. If the mold usage rate is not high, the mold frame material is 45# steel, and the mold core, mold cavity, and slider are nitrided P20 steel.
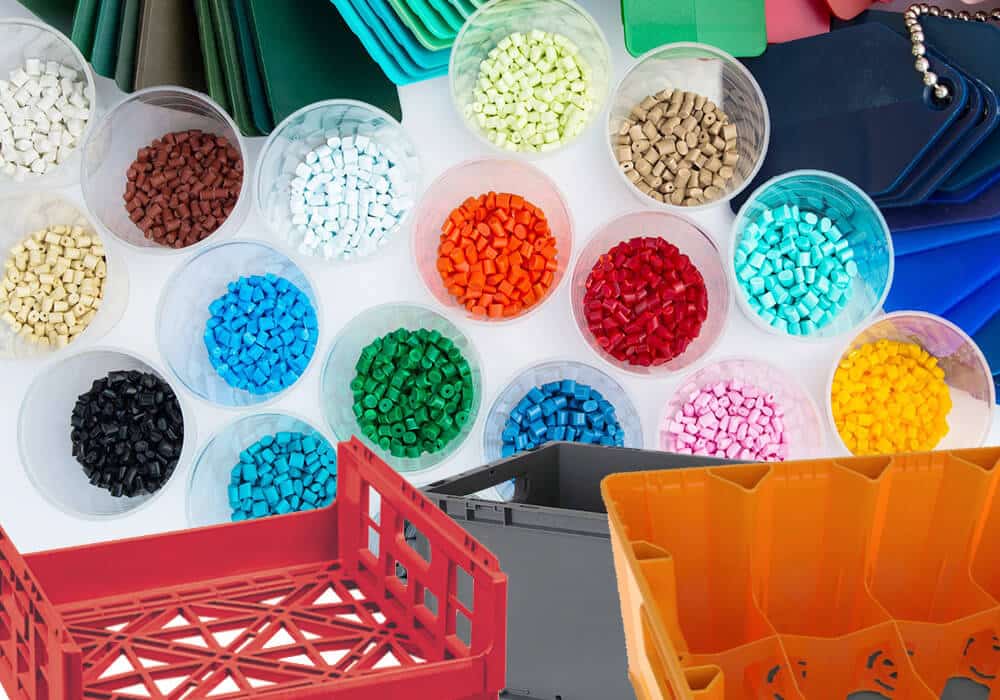


The choice of plastic depends on the specific requirements of the crate, including its intended use, required strength, chemical resistance, and cost considerations. Often, additives are added to these base materials to enhance specific properties, such as UV resistance, color stability, or antimicrobial properties. Commonly used materials are:
- High-density polyethylene (HDPE): has an excellent strength-to-density ratio, good chemical resistance, and low moisture absorption. Widely used for heavy-duty crates in agriculture, the beverage industry, and general logistics. If you need to mold a durable plastic crate, you need to use low MFI HDPE, such as MFI=4 or even MFI=6...
- Polypropylene (PP): High fatigue resistance, good chemical resistance, and excellent hinge capabilities. Commonly used in collapsible crates, food storage containers, and industrial packaging.
- Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS): Used for crates that require higher impact resistance and rigidity.
- Polyethylene terephthalate (PET): Sometimes used for transparent or translucent crates.
- Recycled plastics: More manufacturers are incorporating recycled HDPE or PP into crate production to improve sustainability.
Plastic crate molding process
Plastic crate production involves a complex injection molding process that requires sophisticated equipment and careful control. Let YUCO introduce each step of our production and discuss common problems that may arise.
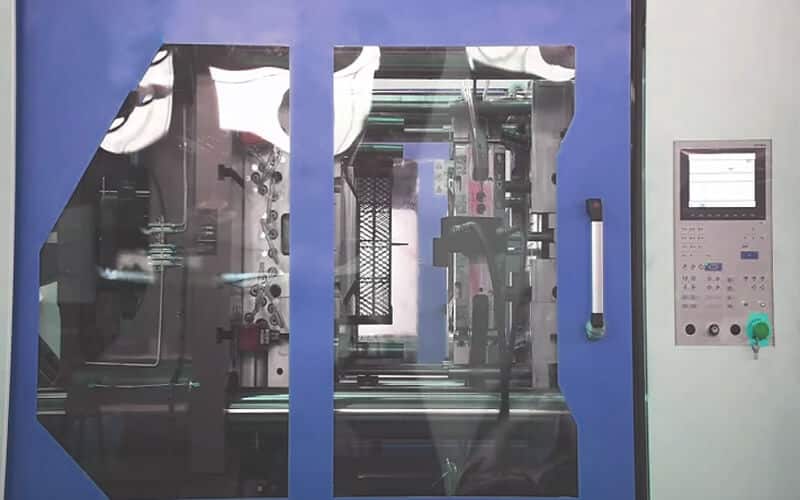

Equipment for molding
High-speed injection molding machine usually has a clamping unit and an injection unit. Depending on the size of the crate, machines with a clamping force ranging from 500 tons to 3000 tons are usually used to produce the crate. The injection screw speed must be greater than 350. The injection speed may be as high as 800mm/s when injecting plastic turnover crates. YUCO uses accumulators to increase the melt injection speed.
Custom-designed crate mold that defines the shape and features of the crate.
Material handling system includes hoppers, dryers, and conveying systems to prepare and transport plastic pellets.
Temperature control unit maintains the optimal temperature of the mold and various parts of the machine.
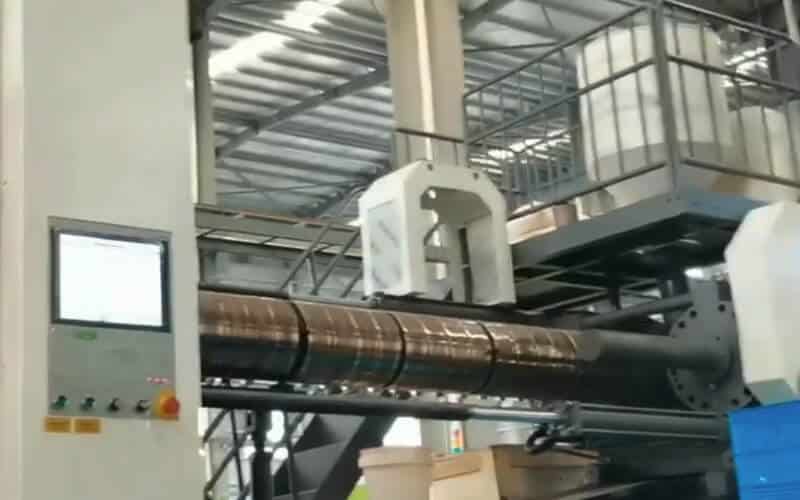

Injection into the mold cavity
The process starts with the following steps: Plastic pellets are fed into the hopper of the injection molding machine, then heated and melted in the barrel of the machine. The molten plastic is then injected into the mold cavity at high pressure through the gate system. The mold is then filled under high pressure, conforming to the shape and details of the mold. In this process, the speed, pressure, holding time and temperature of the injection process need to be strictly controlled to ensure complete filling and achieve the dimensional accuracy of the turnover box.
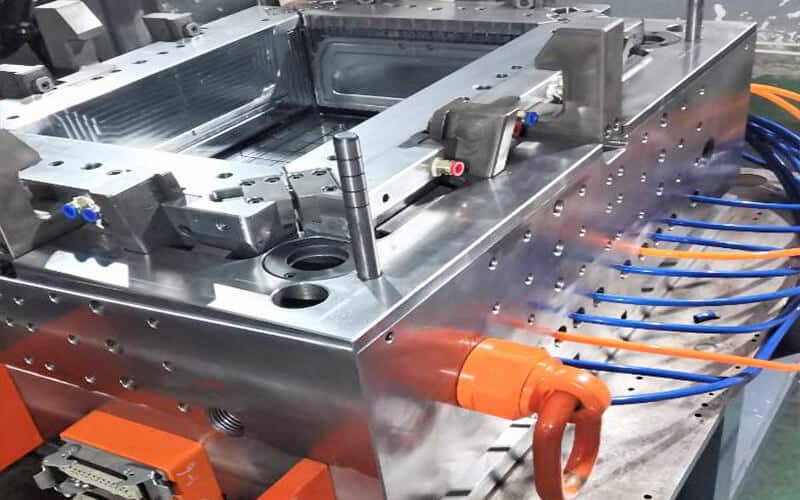

Cooling
After injection, the cooling stage begins. The mold is usually equipped with cooling channels to quickly cool the molten plastic. The cooling time of the turnover box depends on a series of factors such as the thickness of the turnover box, the thermal properties of the plastic, the crystallization properties, and the mold temperature. Proper cooling ensures dimensional stability and prevents warping or other defects. If the cooling time is too long, it will not only reduce production efficiency, but also cause demolding difficulties. To produce durable plastic turnover boxes, the mold must be designed with the largest cooling circuit and the best molding surface
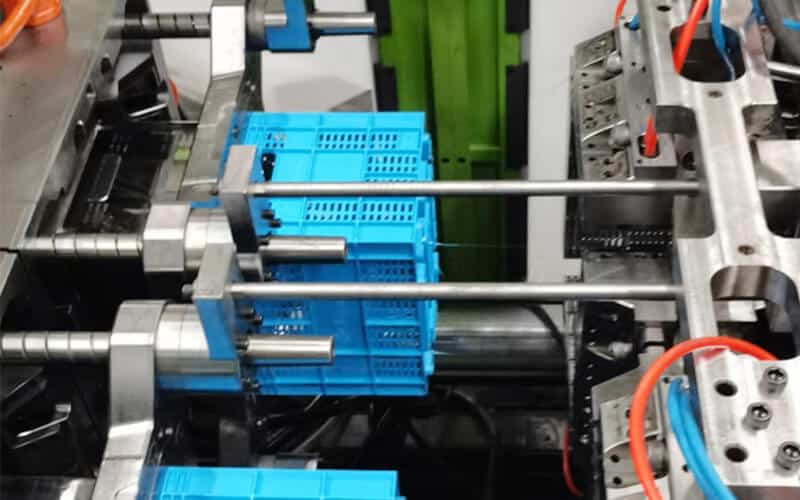
Ejection
After cooling and solidification, the crate is ejected from the mold. First, the mold opens along the parting line, and the ejector pin pushes the crate out of the mold. Then, the crate is removed manually or by an automated system. After that, the mold closes and a new cycle begins.
The ejection method of the turnover box plastic molding is best designed as an automatic ejection mechanical system, and the draft angle is as large as possible, so that when the mold is opened, the ejection is smoother and more efficient, and automatic demolding is achieved.
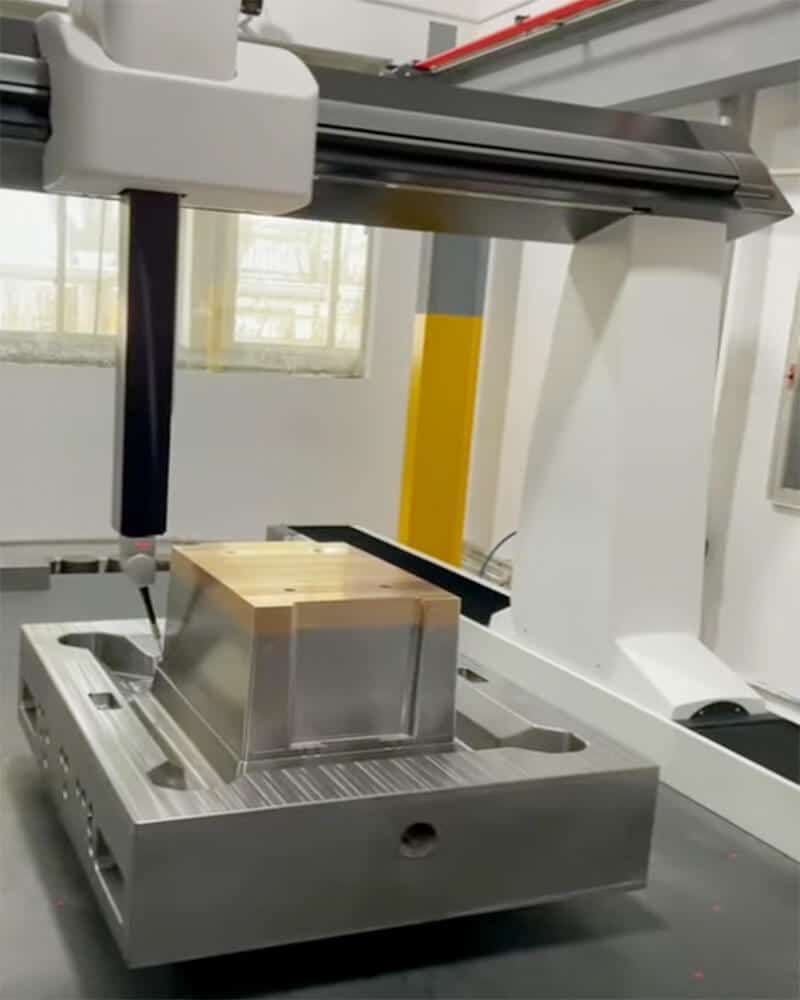

How to design and make crate molds?
Designing and manufacturing a crate mold involves several steps to ensure that the mold meets the requirements for producing a durable and fully functional crate. Here is a general overview of the process:
Define requirements and specifications
- Shape: Understand the purpose of the crate (e.g., shipping, storage) to determine the shape of the crate. Complex shapes may require advanced mold design, including slides or lifters. In addition, features such as ribs, handles, and stacking mechanisms must be incorporated into the mold design.
- Size: The overall size of the crate determines the size of the mold and the required machine capacity.
Wall thickness: Wall thickness affects material usage, cooling time, and crate strength, and typically ranges from 2.5 mm to 5 mm, depending on the application. - Material: Based on durability and cost considerations, the appropriate material is selected.
- Quantity: Estimate production quantity and determine the mold type (e.g., prototype mold, production mold).
- Strength: Design some crisscross ribs on the outer surface and bottom of the plastic packaging crate to increase its strength and rigidity.
Mold design
- Gating and runner systems: Design the gate (where molten material enters the mold) and runner system (channels that distribute material to multiple cavities). Using hot runner system technology can improve the quality of plastic parts, reduce production costs, and save time.
- Cooling system. The cooling system is designed to regulate mold temperature and ensure proper material solidification. Conformal cooling is an advanced technology that uses curved cooling channels that follow the contours of the part. Options such as beryllium copper inserts improve thermal conductivity. Baffle and bubbler systems are used to cool deep cores or complex geometries.
- Ejector system. Ejector pins need to be carefully placed to provide even force distribution. Remove the crate from the mold after cooling. Incorporating draft angles can help smooth demolding.
Software simulation
Modern mold design optimization relies heavily on computer simulation software. Modify the design based on the simulation results to ensure the best part quality.
- Mold flow analysis simulates how plastic flows through the mold, helping to optimize gate locations and identify potential defects (e.g., air pockets, welds).
- Structural analysis ensures crate design meets strength requirements
- Cooling analysis optimizes the layout of cooling channels for efficient heat dissipation.
- Shrinkage and warpage predictions help predict and mitigate potential shape distortion.
Making the mold
The plastic crate mold making process involves several key stages. Machining is a key step, with CNC milling used to create the basic shape and features of the mold. EDM is particularly useful for creating complex or hard-to-reach geometries within the mold. After machining, heat treatment is performed to increase the hardness and durability of the mold.
Polishing and finishing are the final steps in the mold making process. Polishing removes any microscopic imperfections left by the machining process, while finishing techniques can create specific textures or surface features as needed. The level of polishing and finishing depends on the desired appearance of the final crate product.
Testing and validation
Trial runs are conducted to test the functionality of the mold and evaluate the quality of the produced crates. These initial runs allow engineers to evaluate various aspects such as part size, surface finish, strength, and overall quality. Any issues discovered during these trial runs, such as filing issues, inefficient cooling, or ejection difficulties, are carefully analyzed.
Based on the results of these trial runs, necessary adjustments are made to optimize part quality and mold performance. This may involve fine-tuning process parameters such as injection pressure, temperature, and cooling time. In some cases, minor modifications to the mold itself may be required. This iterative process of testing and adjusting ensures that the molds are capable of consistently producing high-quality crates that meet all specified requirements.
Production
Once the mold design has been validated, full-scale production of crates begins using the finalized molds. During this phase, it is ensured that consistent quality is maintained during large-scale production. This involves regular monitoring of the production process, periodic quality checks, and preventive maintenance of the molds.
Plastic crate injection molding troubleshooting
Despite proper control, various defects may still occur in crate production. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
Demolding deformation
If the deformation occurs during the mold trial stage, consider whether the mold ejector is too thin, unevenly distributed, or the demolding slope is improperly set; if the deformation occurs during the production process, it is improper process parameter settings, such as short cooling time and too high mold temperature, resulting in poor cooling of the plastic crate. Corresponding adjustments should be made, such as increasing the cooling time, optimizing the cooling channel design in the mold, and ensuring uniform mold temperature.
Material shortage
This phenomenon may begin to occur in the crate during the mold trial stage because the screw position is inaccurate. If this is not the case, it may be that the injected material is insufficient or solidified prematurely. You can try
- Increase the injection pressure or speed.
- Check if there is a blockage in the gate or runner system
- Slightly increase the melt temperature.
Wrinkles at the far end of the gate
This is caused by the large mold and premature cooling of the front end of the material flow. It can be solved by increasing the mold temperature and the melt temperature. Or modify the mold design to adjust the gate position or size.
Handle area exhaust
This is an important issue because when the turnover box is loaded with goods and people carry the turnover box, the 2 handle areas will be the biggest stress points. If the exhaust in this area is not perfect on the mold, an obvious joint line will appear and the product will be easily damaged, so consider peripheral exhaust on the processing parting surface.
One-stop service - crate mold design / manufacturing and crate molding.
For crate mold design and manufacturing: YUCO provide end-to-end services, from initial concept development to final mold production. Our design team are experienced professionals who have participated in countless projects. You just need to tell us the type of plastic crate you need and work closely with us to provide molds that optimize the production process.
For crate processing services: Our state-of-the-art facilities can handle all aspects of crate production. Whether you need small batch production or large-scale manufacturing, we have the ability and flexibility to meet your needs. Our processing services include injection molding, assembly, quality control to ensure that your crate is perfectly suitable for your application.
Contact us today to experience the difference that professional mold design and crate molding can make for your business.
Tel: +86 13586040750