corner design
Optimize injection molding corner design to improve molded part quality, strength and efficiency. Expert tips and solutions from a leading Chinese supplier.
Professional corner design in molded parts in China
Injection molding is a versatile and widely used manufacturing process that has revolutionized the production of plastic parts across numerous industries.
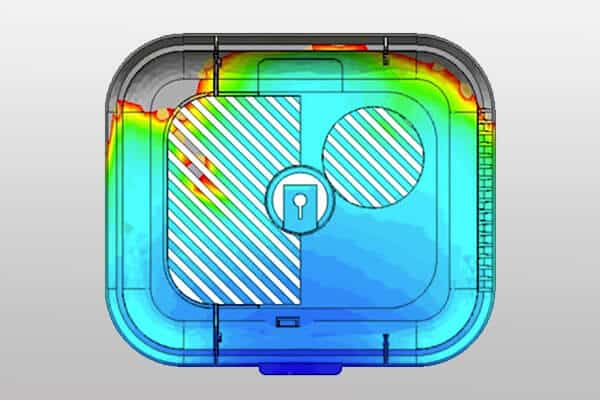
In the world of injection molding, one critical aspect of part design that is often overlooked is the corner. Corners are common areas of stress concentration. Effective corner design has a variety of benefits, including improved part performance, prevention of molding defects such as sink marks and warpage, and improved structural integrity of the part.
As a professional injection mold manufacturer based in China, YUCO MOLD has accumulated extensive experience in complex molded part corner design. Continue exploring to learn how we can help you successfully manufacture injection molded parts! We cover everything you need to know about corners, from the corner basics to corner design factors and troubleshooting.
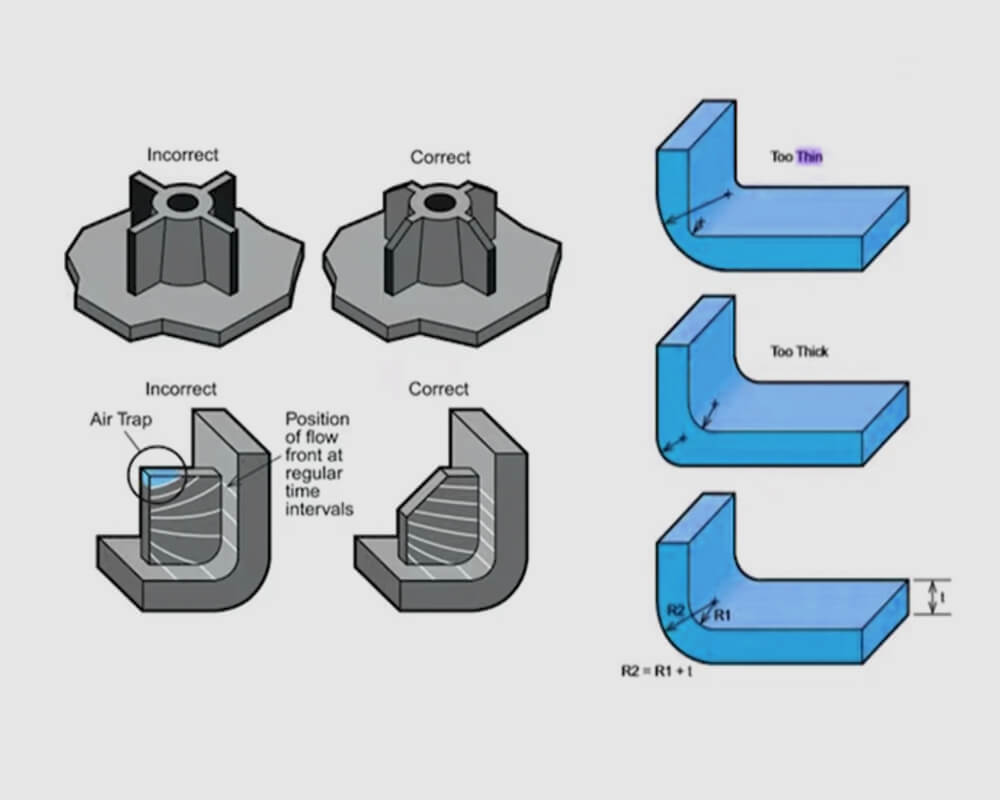
understanding corners

- Stress concentration: Corners, especially sharp ones, can cause localized stress concentrations within a part. These areas are more susceptible to cracks, which can lead to premature failure under normal operating conditions, compromising product integrity and safety.
- Material flow: The design of corners can significantly affect the flow of molten polymer during injection. Material can slow down or temporarily stop at corners, resulting in incomplete fill or weak spots. Corners are more likely to trap air, leading to voids or bubbles in the final part.
- Aesthetic considerations: Smooth, well-designed corners contribute to a more refined, professional appearance. They can enhance the overall aesthetic of a part, which is especially important for consumer products or visible components. Proper corner design helps minimize common visual defects such as flash, sink marks, and flow lines.
- Mechanical strength: The design of corners directly affects the mechanical properties of an injection molded part. Rounded corners provide superior strength by distributing stress more evenly. Sharp corners are susceptible to stress concentration failures. A balance between sharp and rounded corners improves strength while maintaining a certain geometric definition.
- Dimensional accuracy: Corners can be difficult to hold to tight tolerances due to material shrinkage and flow patterns. Considering adequate draft angles and appropriate radii, etc., is critical to maintaining dimensional accuracy in corners and achieving part functionality and assembly.
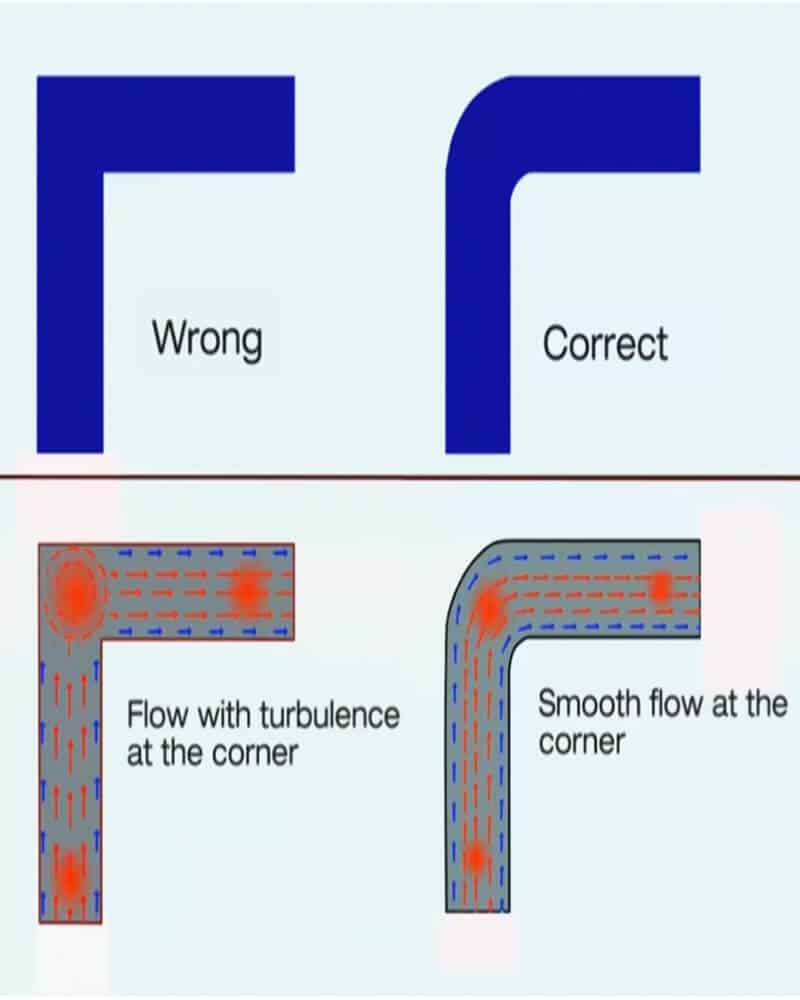
Sharp corners
Characterized by an abrupt transition between intersecting surfaces that approaches 90 degrees. Sharp corners provide clean, well-defined edges that are desirable in certain designs, especially for parts that require a modern, angular aesthetic. However, sharp corners can cause stress concentrations that can make it difficult for the part to withstand loads and can cause dents or other weak points in the surface. They can also create challenges in mold manufacturing and cause increased mold wear during production.
Fillet corners
Fillet corners are rounded internal corners that provide a smooth transition between intersecting surfaces. The fillet radius refers to the radius of the curved portion that forms the fillet. Fillets can distribute stress more evenly, provide a better surface finish, and enhance durability and safety.
When designing an injection molded part, the choice between sharp and fillet corners depends on a variety of factors, including the function of the part, aesthetic requirements, structural needs, and manufacturing considerations. Often, a combination of the two types can be used in different areas of a single part to optimize its overall performance and manufacturability.
Contact YUCO molded part corners design team now!
Factors affecting corner design in injection molded parts
Designing the corners of an injection molded part requires careful consideration of a variety of factors. Understanding these factors is critical to optimizing part performance, manufacturability, and overall quality. Let’s explore the key factors that influence corner design:
Material properties
Different materials have different flow characteristics, shrinkage and mechanical properties, and material selection can significantly affect corner design.
Materials with a high melt flow index tend to fill corners more easily, allowing for tighter radii. The strength and flexibility of the material will affect the minimum radius that can be used without compromising the integrity of the part.
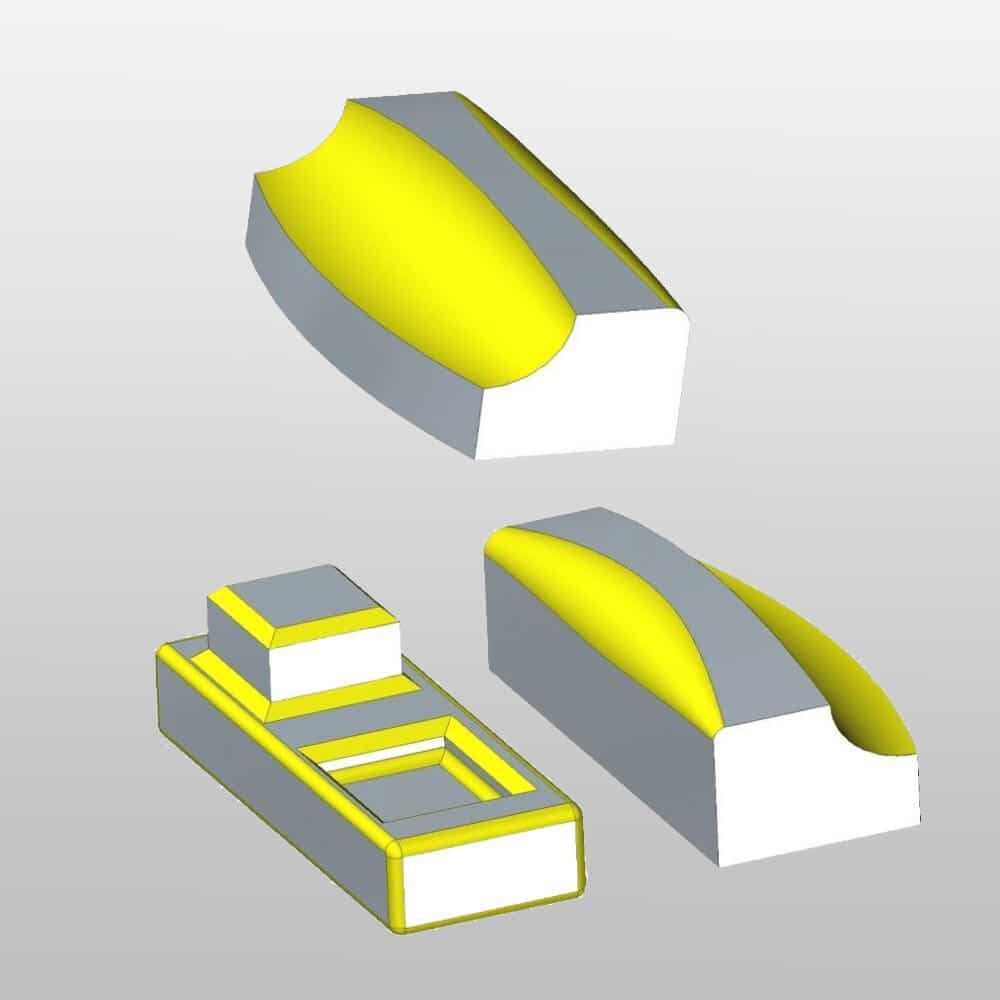
Wall thickness
Wall thickness variation plays a critical role in determining proper corner design. Wall thickness affects stress concentration, stress absorption, melt plastic flow, and cooling rate. Thicker walls may resist deformation better but may increase material usage, part weight, and cooling time. Thicker walls require larger radii to avoid stress concentrations and prevent molding defects.
Maintaining consistent wall thickness around corners is critical to preventing issues such as sink marks and warpage. Additionally, larger radii are required for thicker walls. When changes are required, ensure a gradual transition in wall thickness near corners.
Mold processing considerations
Corner design directly affects mold manufacturing and maintenance, affecting cost and efficiency.
Sharp corners or very small radii in molds can be challenging and costly to machine. Special machining methods such as EDM and extended machining time are required to achieve the desired radius.
Corners also wear faster, resulting in increased maintenance costs and shortened mold life. In addition, wear causes mold dimensional changes, and it can be difficult to continue to produce parts with high dimensional accuracy.
Sharp corners can create challenges when removing parts from the mold and may require more complex mold ejection designs.
Injection molding process parameters
Various process parameters affect corner quality and must be considered during the design phase. For example:
- Gate location: Correct gate location ensures balanced filling of the corner, reducing the risk of defects.
- Mold cooling: Effective cooling channel design around corners is critical to maintain dimensional stability and prevent sink marks.
- Injection and holding pressure: These parameters must be optimized to ensure complete filling of the corner without causing flash or other defects.
- Cycle time: Well-designed corners can improve material flow and cooling efficiency, potentially reducing overall cycle time.
Simulation and prototyping
Leveraging technology and physical testing is critical to optimizing corner design.
Use software such as Moldflow to simulate material flow, evaluate stress distribution, predict potential problems, and optimize corner design before mold manufacturing.
Produce prototype parts to validate corner design, testing for strength, appearance, and manufacturability. And continually use insights from simulation and prototypes to improve corner design for optimal performance.
Corner radius guidelines
The fillet radius is the amount of curvature used at the corners of a part. The choice of part radius depends on factors such as the material properties used, part thickness, aesthetic requirements, application requirements, and production cost-effectiveness. However, some general rules of thumb include:
- The minimum radius for inside corners is typically 0.5 to 1 times the wall thickness.
- The radius for outside corners is typically 1.5 to 2 times the wall thickness.
- Materials with high shrinkage or poor flow characteristics have larger radii.
Specific recommendations
For sharp corners:
- Avoid sharp corners by using fillets whenever possible, which helps evenly distribute stress and reduce stress concentrations.
- Implement gradual transitions whenever possible to reduce stress concentrations.
- Consider reinforcing sharp corners with ribs or gussets.
- For applications that require sharp corners, select materials with high impact resistance.
For fillet corners:
- For general-purpose plastics, start with a fillet radius of 25-50% of the wall thickness.
- For materials with high viscosity or high stress areas, increase the radius.
- Consider using asymmetrical fillets to balance material flow and strength requirements.
Common defects related to corner design
Sink marks
Sink marks are depressions or pits on the surface of molded parts, usually appearing near corners or thick sections. The causes are as follows:
- Uneven cooling rates of thick and thin wall sections
- Excessive wall thickness at corners
- Insufficient holding pressure
- Poor design of cooling channels at corners
Prevention methods
- Maintain uniform wall thickness, especially at corners
- Implement appropriate corner radius to promote uniform material distribution
- Optimize holding pressure and time to compensate for material shrinkage
- Design efficient cooling channels at corners
- Consider using gas-assisted injection molding for thick-walled sections

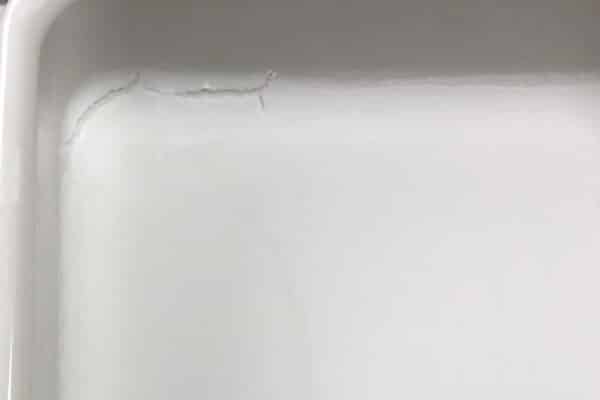
Stress cracking
Stress cracking occurs when local stresses exceed the strength of the material, usually starting at corners due to stress concentrations. Causes:
- Sharp corners create stress concentration points
- Excessive in-mold stresses due to poor corner design
- Material degradation caused by overheating in corners
- Environmental stress cracking caused by chemical exposure in the application
Prevention methods
- Use large radii in corners to reduce stress concentrations
- Design for uniform wall thickness to minimize differential cooling and shrinkage
- Optimize processing conditions to reduce in-mold stresses (e.g., lower injection pressure, proper cooling)
- Select appropriate materials for the application with good resistance to stress cracking
- Consider annealing the part after molding to relieve internal stresses

Warpage
Warpage is the distortion of the part shape after molding, usually more pronounced in areas with corners or transitions. Causes:
- Uneven cooling rate throughout the part, especially at corners
- Uneven shrinkage due to inconsistent wall thickness
- Excessive molding stress, especially at sharp corners
- Poor mold ejection due to corner design
Prevention methods
- Design for uniform wall thickness, including gradual transitions near corners
- Implement symmetrical cooling channel layout around corners
- Use appropriate corner radius to reduce molding stresses
- Optimize processing conditions (e.g., mold temperature, cooling time) for uniform solidification
- Consider using ribs or gussets in warp-prone areas
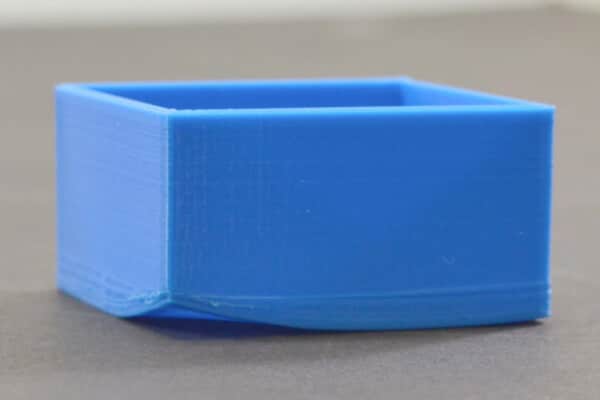

Short shots
A short shot occurs when the molten plastic fails to completely fill the mold cavity, which often leaves corners or edges incomplete. Reasons include:
- Insufficient injection pressure or material volume
- Poor material flow, especially at corners
- Premature freezing of the melt due to cold mold surfaces
- Insufficient venting, air trapped in corners
Prevention methods
- Increase injection pressure or injection volume
- Optimize corner design and use appropriate radius to improve flow
- Ensure proper mold temperature, especially near corners
- Implement adequate venting in corner areas
- Consider using flow guides or variable wall thickness to guide material into hard-to-fill areas
Elevate your injection molding projects with expert corner design
The importance of getting corner design right cannot be overstated. By prioritizing corner design, you can not only optimize part quality, but also improve manufacturing efficiency, reduce scrap rates, and increase profits.
At YUCO MOLD, we bring decades of injection molding expertise to every project we undertake. As a leading injection molding solutions provider in China, we have honed our corner design skills across a wide range of industries and applications.
- Conduct a comprehensive design review focused on corner optimization
- Leverage advanced CAE simulation to predict and prevent corner-related issues
- Implement innovative corner designs that balance aesthetics, strength, and manufacturability
Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize the corner design in your project and improve the quality and efficiency of your injection molded parts.
Tel: +86 13586040750