texture design
Enhance your product development with YUCO’s injection mold texture design. Advanced surfaces, digital prototyping, sustainability, mass personalization. Partner with us.
Professional injection mold textures design in China
In the world of plastic product manufacturing, the tactile and visual qualities of plastic parts have become as important as their functional performance. Many of these processes can improve the appearance of the product, such as adding textures to the mold.
As a leading injection molding solution provider in China, YUCO understands the importance of mold texture design. It determines the function, feel and appearance of your product. Our expertise enables us to provide innovative texture solutions that not only meet but also exceed industry standards.
Now let's start by discussing the basics of surface textures to familiarize you with YUCO's powerful texture design and processing capabilities.

Understanding texture

In injection molding, mold texturing refers to intentional designs and modifications to the mold surface. Some of these structures are regular, repeating patterns, while others are random and difficult to describe in general terms.
Texture is typically applied to mold through various methods, such as chemical etching, laser engraving, or machining. The structure is then transferred to the plastic part during the molding process.
Mold surface texture covers a wide range of finishes, from smooth, high-gloss surfaces to intricate patterns and granular textures. The choice of texture can significantly affect the look and feel of a product, affecting factors such as tactile perception, visual appeal, and even performance characteristics.
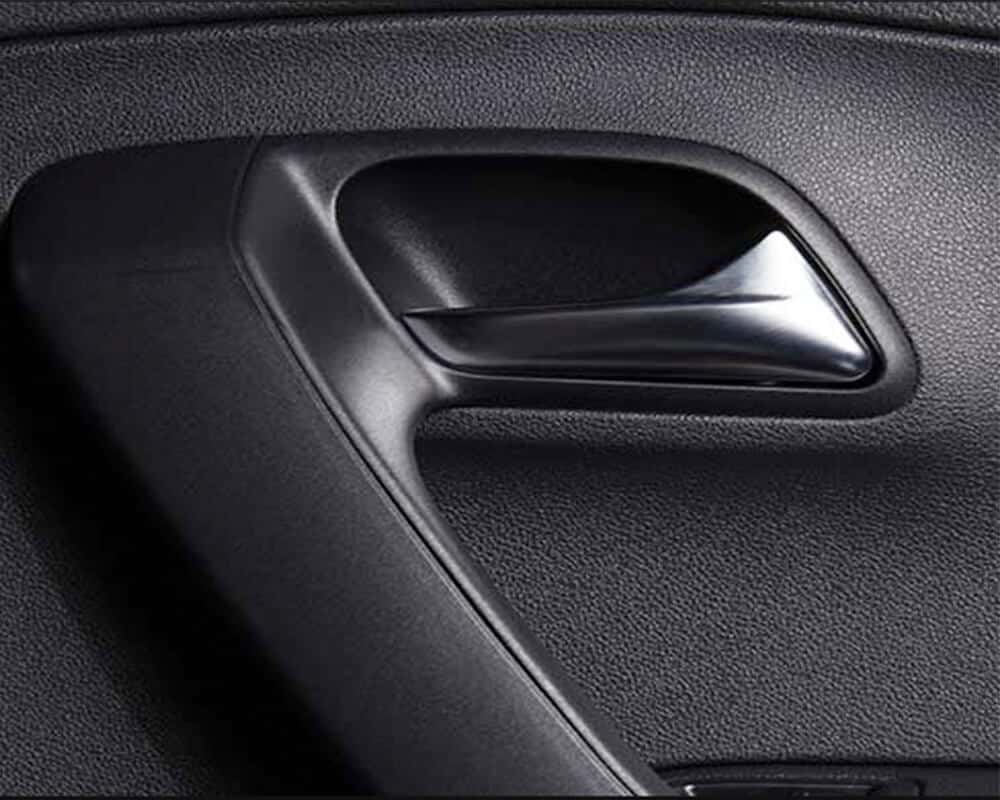

Textures in injection molding are more than just surface decoration, they play a key role in the functionality, beauty, and branding of plastic parts. Significant advantages include:
- Mold texturing allows manufacturers to transform ordinary plastic surfaces into visually stunning aesthetic elements by applying a variety of patterns and finishes.
- Texture affects the feeling that users experience when they come into contact with a product. For example, the soft touch on a smartphone case or the textured surface on packaging.
- Surface texture can act as camouflage for flow lines, dents, burn marks and other defects.
- Adding surface texture helps improve the non-slip properties of the material. This makes it easier to hold the part.
- Textures have enhanced adhesion and strength, which can increase the durability of the product. Textured surfaces effectively hide scratches and scuff marks that accumulate over time.
- Texture offers a unique opportunity to integrate branding directly into product design. It creates a unified look that enhances brand loyalty and market influence.
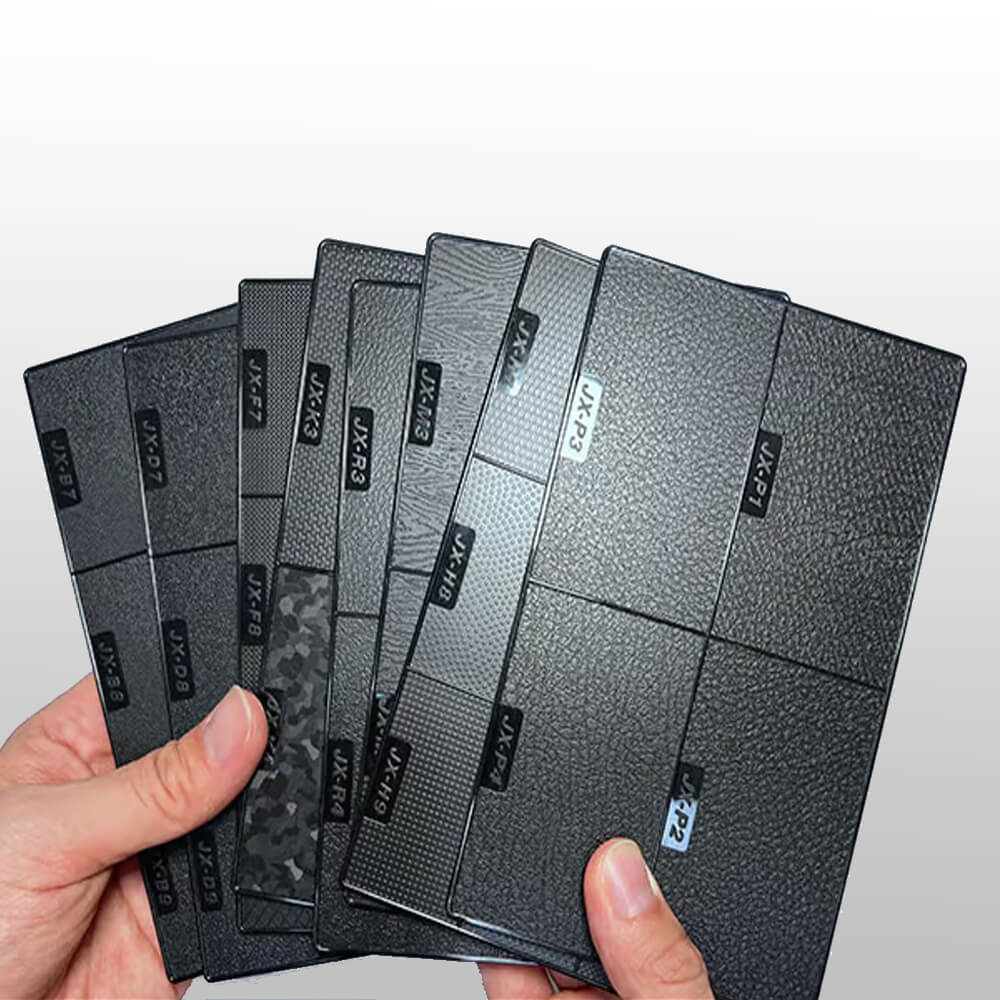

Each texture has unique properties. Below, we will examine the most common types of mold textures.
High gloss finish (polished finish)
It is achieved by carefully polishing the mold cavity to a mirror finish. Textures in this category are shiny, smooth, and often expensive. High gloss surfaces enhance the color vibrancy and depth of the material, giving the product a premium and sophisticated appearance. High gloss surfaces are popular in consumer electronics and home appliances for sun visors, plastic mirrors, and other optical components.
Matte and satin finishes
Matte and satin finishes are achieved by lightly texturing the mold surface, which diffuses light and reduces reflectivity. In addition, matte surfaces are less susceptible to fingerprints, smudges, and minor scratches, helping the product maintain a clean, neat appearance over time. In automotive interiors, matte and satin finishes are best used on dashboards, control panels, and interior trim to prevent distracting reflections and enhance the driving experience.
Textured patterns
- Simulated materials (e.g., natural materials such as leather, wood grain): These texture patterns add a touch of luxury and authenticity to plastic products. These simulated textures are created by etching or engraving the desired pattern on the mold.
- Geometric and organic patterns: Geometric patterns, including stripes, grids, and abstract designs, as well as organic patterns inspired by nature, provide unique visual and tactile experiences. These textures can be customized to create a unique look that makes your product stand out in the market.
Microtexturing
Microtexturing involves extremely fine patterns etched into the mold surface at a microscopic scale. These advanced textures can impart specific functional properties to molded parts, such as improved grip, tactile feedback, or hydrophobicity. Microtexturing can also affect the interaction of light with the surface, creating subtle visual effects. Soft-touch textures are especially valuable for products that are frequently used or require precise manipulation.
Contact YUCO mold texture design team now!
design considerations for mold textures
Creating mold textures requires a thoughtful approach that balances aesthetics, functionality, manufacturability, and cost. Understanding these factors can help you achieve the desired aesthetic and performance results. Here are some considerations when designing mold textures for injection molded parts.
Understand product requirements
The first step in mold texturing design is to understand how the texture will affect the use of the product. The purpose of mold texturing is to improve the appearance of the part while ensuring it performs its function. Therefore, you need to consider the type and aesthetics required for the product. This will help you choose the texture you need.
Evaluating production needs next ensures that the texture design is aligned with manufacturing capabilities. Textures that are suitable for low-volume production may not be suitable for large-scale production due to tooling complexity or cycle time. High-volume products will require textures that are consistently reproducible and do not degrade over time. However, more complex textures may increase tooling costs and production time, affecting the overall budget.
Material selection
Each material has unique physical and chemical properties. The melting temperature of a material is a key component of its ability to produce a specific texture. Most thermoplastic materials, including ABS, PC, PP, PE, and nylon, can be textured.
The choice of plastic material can significantly affect texture reproduction and appearance:
- Texture reproduction: Different plastics vary in their ability to reproduce fine details. Amorphous polymers, such as ABS or polycarbonate, are better at capturing texture than semi-crystalline polymers, such as polyethylene.
- Additives and fillers: Adding additives (e.g., UV stabilizers, colorants) or fillers (e.g., fiberglass) can change the viscosity and flow characteristics, which can affect the outcome of the finished product.
- Material properties: The shrinkage, stiffness, and thermal properties of a material can affect how a texture appears on the final part.
Therefore, it is necessary to consider the different materials before selecting a surface texture.
mold design factors
Draft angles
Adding texture to a mold may require adjustments to the draft angle to ensure smooth part ejection. Textured surfaces require larger draft angles than smooth surfaces to prevent part damage or sticking. Deeper textures or textures with undercuts require careful consideration of texture depth and orientation to facilitate demolding.
Here is a breakdown of draft angle considerations for different texture types:
- Light texture (0.001 in. – 0.005 in. depth) or (0.0254 to 0.127 mm): A draft angle of 1 – 2 degrees is usually sufficient for light textures such as brushed finishes or small staples.
- Medium texture (0.005 in. – 0.010 in. depth) or (0.127 to 0.254 mm): For textures such as leather or medium depth woven patterns, a draft angle of 3 – 5 degrees is recommended.
- Heavy texture (0.010″ – 0.020″ deep) or (0.254 to 0.508 mm): For deep textures such as wood grain or complex geometric patterns, a minimum of 5 – 10 degrees is critical.
1.5° draft per 0.001″ (0.0254 mm) of texture depth is a useful rule of thumb but must be adjusted based on specific texture type and other factors.
Placement of parting lines and gates
Strategic placement ensures aesthetic quality and structural integrity. Avoid placing parting lines over critical texture areas to prevent visual defects and ensure texture continuity. Place gates to promote uniform flow and minimize flow lines or weld lines on textured surfaces.
Effects on demolding
Rough or deep textures increase friction and can cause ejection issues. Proper ejection systems (e.g., pins, sleeves, airflow) can be implemented to reduce the risk of part damage. Also, the use of release agents or surface coatings can facilitate demolding but may affect the final surface finish.
creating textured designs
Choosing the proper texture application method is critical to achieving the desired results:
Chemical etching
The most common process is chemical etching, which works by masking the mold surface and using an acid etchant to create the texture. Chemical etching is a powerful technique that can be used to cost-effectively produce uniform textures over large areas. Patterns such as grain, leather, or geometric patterns are examples. Commonly used in automotive interiors, appliance housings, and consumer products.
Laser engraving
Ablating the mold surface using a focused laser beam to achieve complex and precise textures. Photolithography can create sharp lines, fine details, and intricate textures with amazing precision. Unlike some methods that are limited to specific materials, photolithography works with a wide range of metals, including steel, aluminum, nickel, and plastics. This flexibility allows us to experiment with different mold materials. Ideal for custom logos, patterns, and other complex designs. Commonly used in electronic housings, medical devices, and branding elements.
Electrical discharge machining (EDM)
EDM stands for Electronic Discharge Machining, which is a surface treatment that uses electric sparks to erode, creating unique textures. It is time-consuming and costly and is best suited for small areas or special textures, such as aerospace components, precision tools, and specialized industrial parts.
Sandblasting
This is a surface roughening technique where an abrasive (e.g. sand, glass beads) is used to blast the mold surface. The random nature of sandblasting and spraying results in a non-directional and uniform surface treatment to create a matte or textured finish. This is a quick and cost-effective way to create simple textures and is often used for industrial equipment, non-slip surfaces, and components where aesthetic details are less important.
3D printing
This is an innovative technology where additive manufacturing allows complex textures to be created directly on mold inserts or prototypes. Ideal for rapid prototyping, custom short-run production, and experimental designs
maintaining textured molds
Regular cleaning and inspection are essential to maintaining the quality of your molded dies. Avoid abrasive cleaning methods that can damage the structure. Proper storage and handling also help extend the life of your mold.
Prototyping and testing
Prototyping helps identify issues with texture look, feel, and manufacturability. Physical samples can be used to evaluate how texture affects product use, addresses ergonomic issues, and meets aesthetic goals. Gathering input from potential users can help with adjustments to improve satisfaction and market acceptance.
Challenges and solutions in mold texture design
Texture consistency
Achieving uniform texture on complex geometries can be difficult due to variations in mold surface and material flow.
Solutions
- Leverage advanced CNC machining and laser texturing technologies to achieve precise and consistent textures.
- Optimize injection molding parameters such as pressure, temperature, and cooling rate to improve texture fidelity.
- Perform thorough prototyping and testing to refine molds and processes for greater precision.
- Implement stringent quality control measures during production.
Texture durability and wear resistance
Mold textures deteriorate over time due to friction and environmental factors, resulting in inconsistent product surfaces.
Solutions
- Apply hard coatings or surface treatments to molds for increased durability.
- Use high-quality, wear-resistant mold materials to extend the life of the mold.
- Incorporate additional support features to reduce long-term loads on snap-fit
- Consider environmental factors (temperature, humidity) that may exacerbate creep
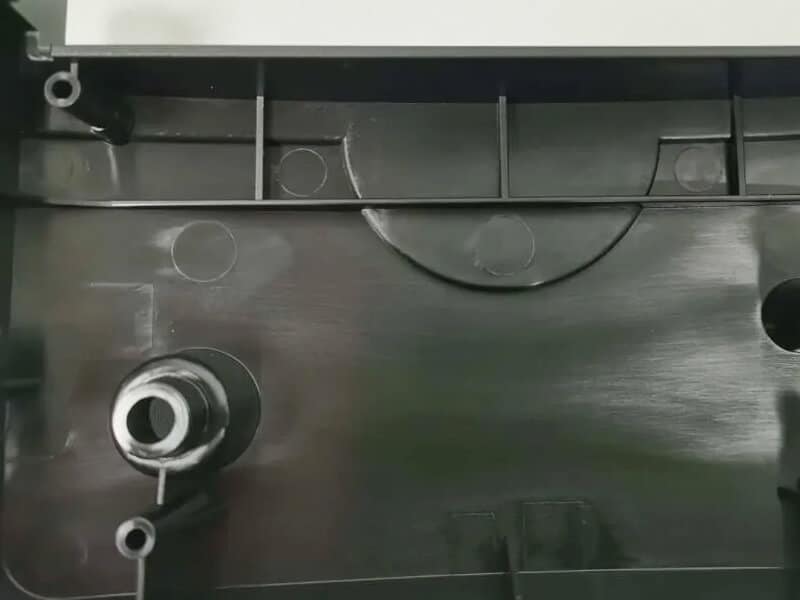

Texture imperfections and surface defects
Defects such as blemishes, dents, or flow lines can occur on textured surfaces, affecting aesthetics and functionality.
Solutions
- Design molds with proper venting and gating systems to reduce the likelihood of defects.
- Adjust material formulations and molding conditions to minimize surface defects.
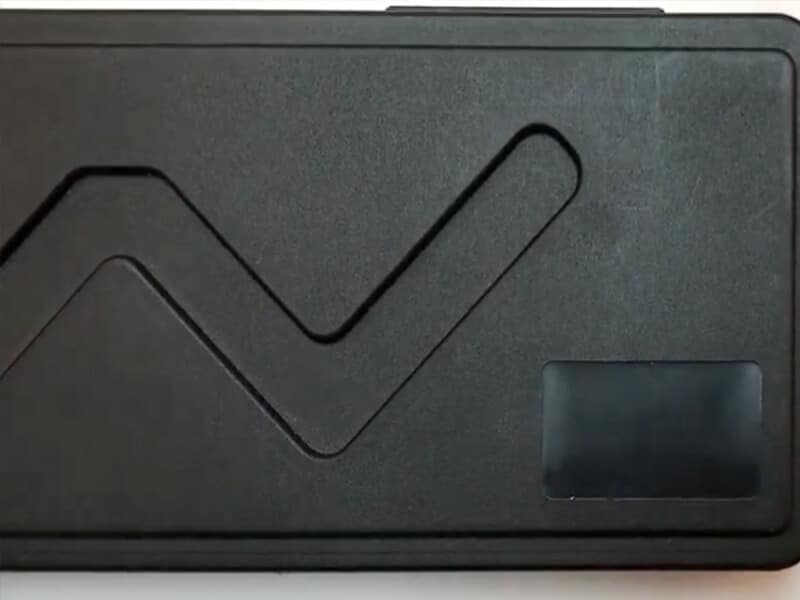

Applications of textures
Throughout our many success stories, YUCO has consistently leveraged expert texture design to enhance product functionality and aesthetics across a wide range of industries.
- For consumer electronics, we leverage textures to enhance the feel of products, making devices not only stylish but also providing an exceptional tactile experience.
- In automotive applications, our expertise in texturing helps optimize internal components and user interface elements. We achieve a harmonious balance between durability and aesthetics, ensuring components withstand rigorous use while maintaining a high-end appearance.
- In the medical device space, we prioritize textures that enhance usability and hygiene. Our solutions meet strict regulatory standards while improving grip and ease of sterilization.
These achievements highlight our ability to provide customized texture solutions that meet specific industry requirements, combining functionality with superior design to exceed customer expectations.
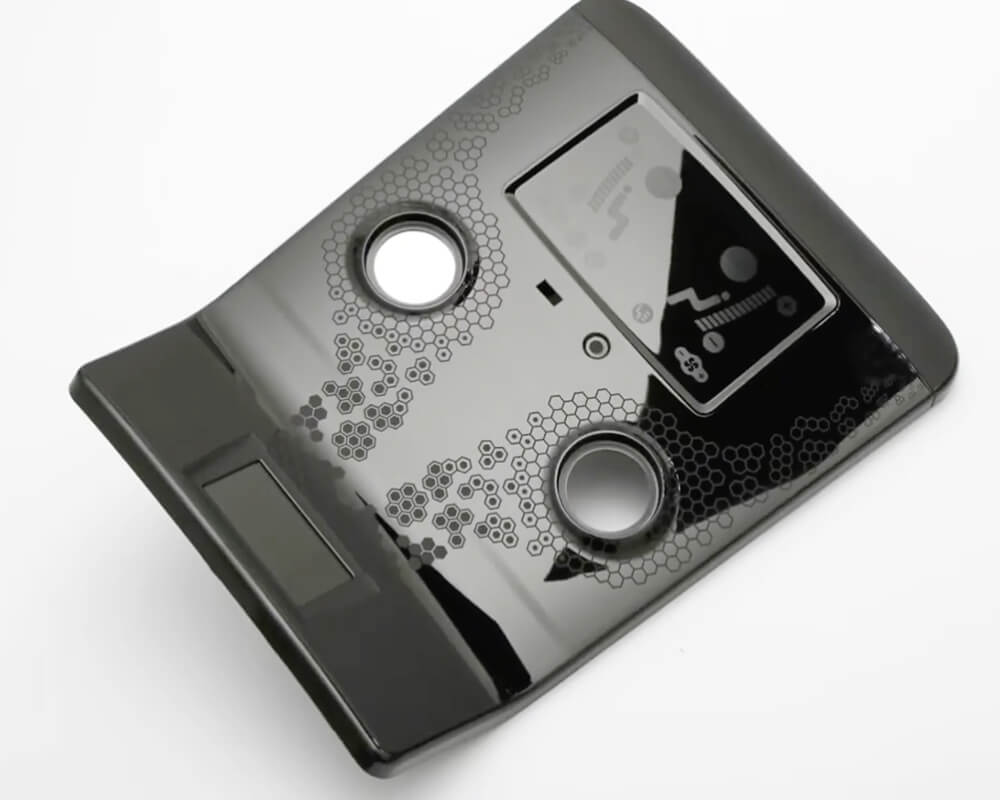

Elevate your mold texture designs with YUCO solutions
Injection mold texture design is not only an aesthetic enhancement, but also a key element of product development. As a leading injection molding solution provider in China, YUCO is committed to providing innovative texture design solutions. Our leading capabilities:
- Nano textures and functional surface textures with self-cleaning properties are available
- Digital simulation texture testing
- Rapid prototyping technology
- Texture methods for environmentally friendly materials or bio-based plastics
- Customized textures for individual products
Contact YUCO now, and together we can create products that not only meet functional expectations but also attract and delight your customers.
Tel: +86 13586040750