injection molding design
Discover expert injection molding design services. Optimize parts, reduce costs, and embrace innovation with YUCO innovative solutions. Elevate your projects today.
Professional injection molding design service provider
Injection molding is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, revolutionizing plastic part production across a wide range of industries. However, the success of injection molding depends on deliberate design.
Injection molding design ensures the final product's aesthetic and functional quality and significantly impacts production performance, cost-effectiveness, and manufacturing. If the design fails to account for the nuances of the injection molding process, it can lead to expensive mold modifications, production delays, and quality issues.
As a leading injection molding design services provider in China, we understand the challenges and opportunities inherent in this field. Now you can gain a deeper understanding of the complexity of the process and gain a clearer understanding of how YUCO's professional design services can take your manufacturing projects to new heights.
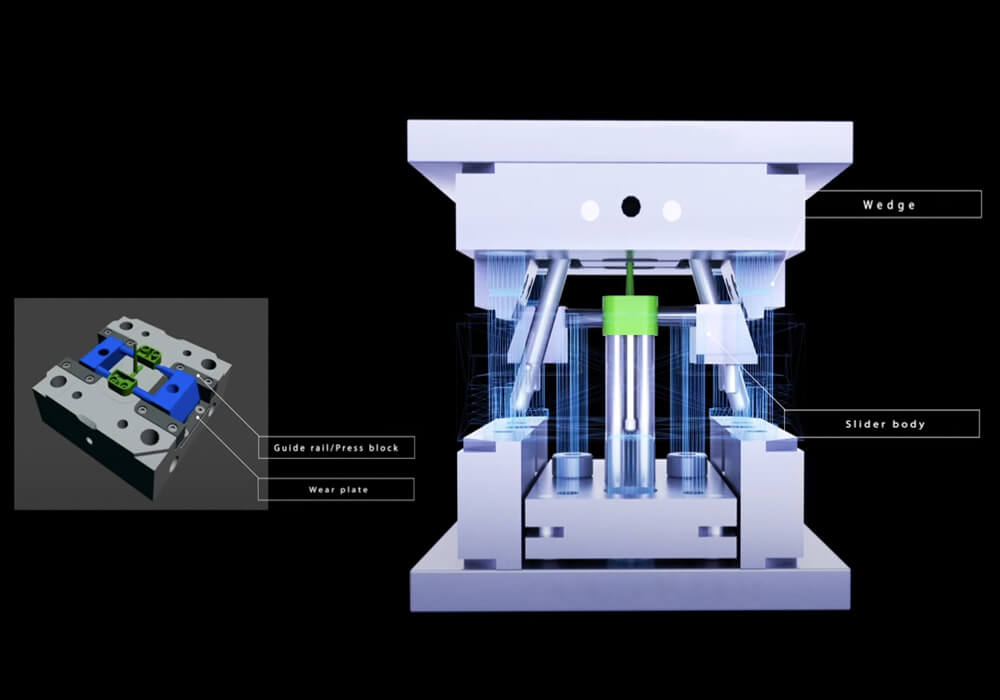
Basics of injection molding design
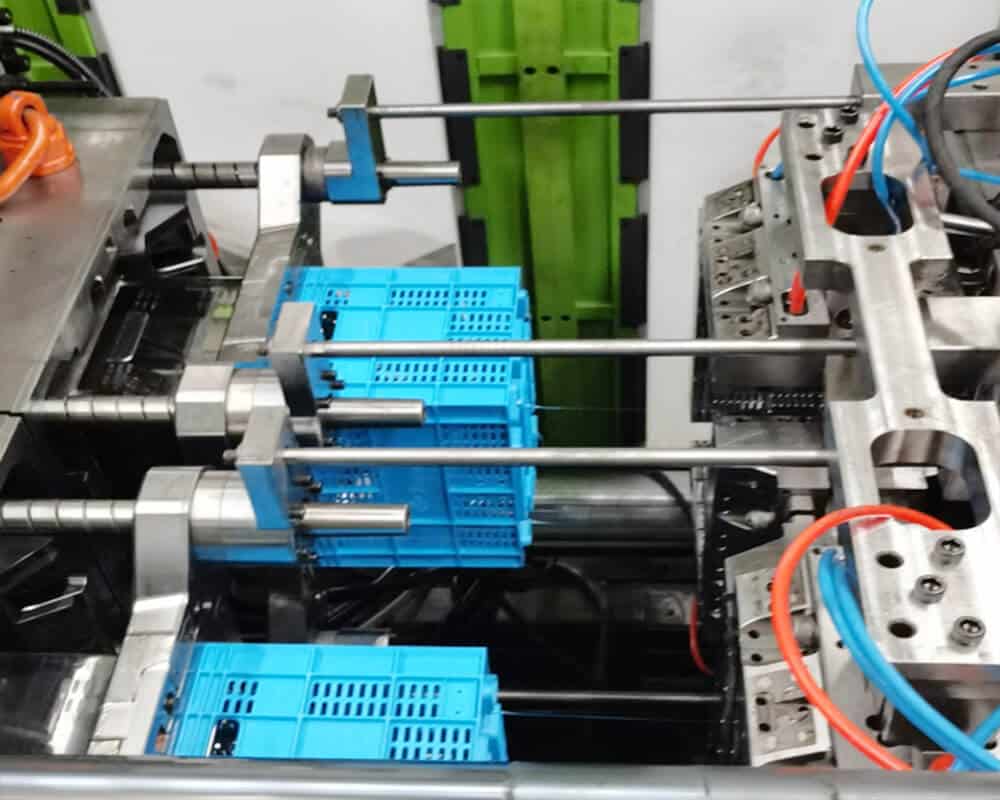
Injection molding is a manufacturing process that involves injecting molten material into a mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies into the shape of the desired part. The process is widely used to produce a large number of plastic parts with complex geometries.
Injection molding includes three basic steps: filling, packing, and cooling.
- Filling: Melted plastic is injected under intense pressure into the mold cavity during filling. The plastic flows into the cavity, taking the mold shape. During the injection phase, the pressure, temperature, and flow behavior of the material change significantly. Understanding these dynamics is critical to optimizing part design and achieving high-quality results.
- Packing: Following the packing phase, the cavity is filled and to cool the material shrinking. This phase is critical to maintaining the section's dimensional accuracy and preventing voids or sink marks.
- Cooling: The molten plastic is stable in the last part of the cooling phase. Cooling rates and uniformity are significant in achieving dimensional stability and minimizing internal pressure. The mold is opened once the plastic is cold enough, and the part is removed.

Material selection is critical in injection molding because it affects the characteristics, appearance, and functionality of the area. Thermoplastics can be melted and reshaped multiple times, such as:
- PE is well known for its flexibility and chemical resistance. It is often used in packaging, containers, and household appliances.
- PP is lightweight, chemically resistant, and has excellent fatigue resistance, making it suitable for automotive parts, medical devices, and consumer products.
- PS is easy to mold and economical and is often used in disposable items such as tableware, containers, and packaging.
- ABS is durable, hard, and impact-resistant, making it a good choice for automotive parts, electronic housings, and consumer devices.
Of course, you can also use thermosets. These materials undergo chemical changes when heated and cannot be re-melted. Examples include epoxies and polyurethanes. However, choosing the right material requires consideration of various factors. Balance mechanical properties, thermal properties, chemical resistance, optical properties, and specific cost requirements. Make sure it matches the requirements of the end-use application.
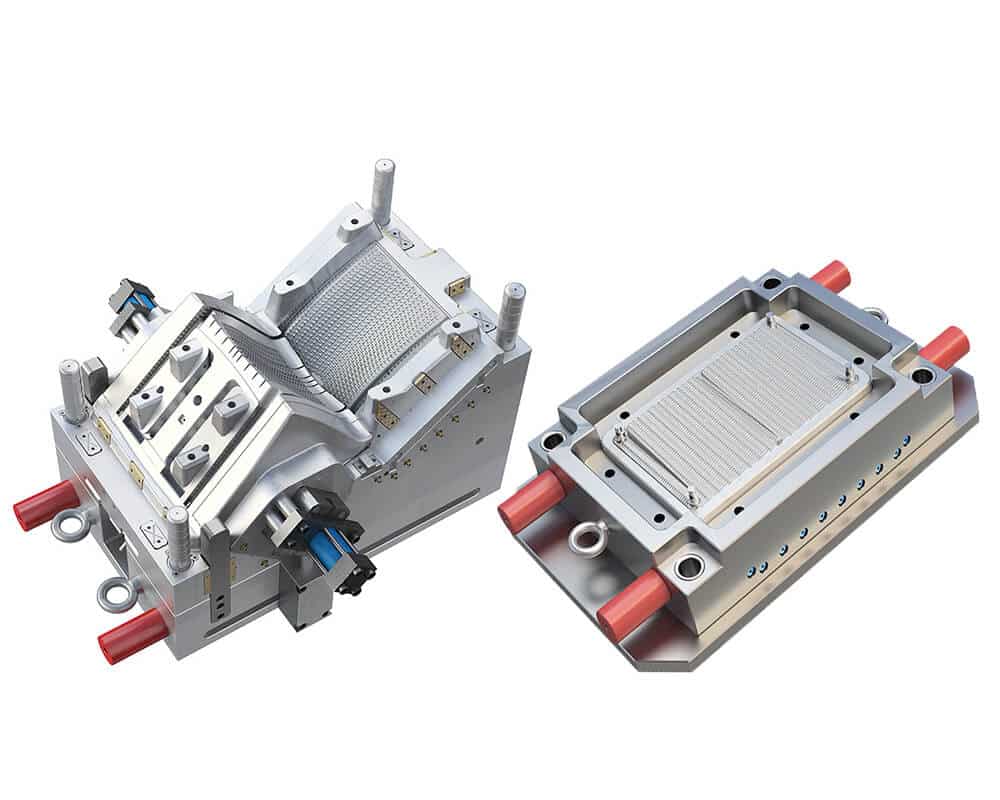
Mold is a precise machine device, usually made of steel or aluminum, in which the cavity is like the final. It consists of a stationary half (scheduled from the machine) and a dynamic half (connected to the clamping unit).
- Cavity: The female part of the mold that forms the outer shape of the part
- Core: The male part of the mold that forms the inner shape of the part
- Gate: The entry point for the molten plastic into the mold cavity
- Runner: A system of channels that direct the molten plastic from one gate to another
- Ejector system: A pin or plate that pushes the solidified part out of the mold
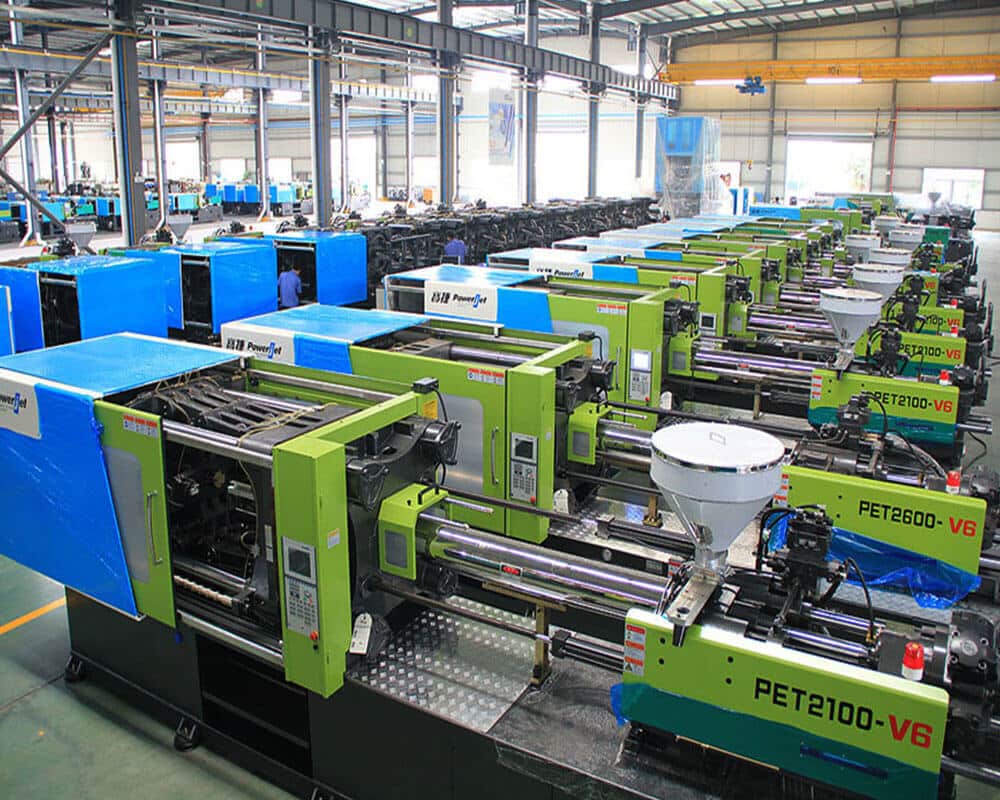

- Hopper: Hopper stores and feeds raw plastic pellets in the machine.
- Injection unit: Presses the molten plastic into the mold. These include screws, barrels, and injection nozzles. Inside the barrel, a rotating screw transports melt and mixes plastic pellets. The barrel is heated to keep the plastic melted as it moves towards the mold.
- Clamping unit: Keeps the mold closed during injection and cooling. Then, it opens the mold to remove the final part and then closes it again for the next cycle.
- Control system: Several vital parameters should be controlled to ensure successful injection molding. Injection temperature should be high enough to ensure proper flow but not so high that it harasses the material. The pressure used to inject molten plastic into the mold affects the mold filling and the quality of this part. The speed at which the molten plastic injection is installed will affect the formation of plastic flow and potential defects. Proper cooling time is critical to avoid dimensional stability and warping.

Design for Manufacturability (DFM) is a method that considers manufacturing requirements early in the design process, with the goal of creating parts that are easier and more economical to produce.
Benefits of DFM:
- Reduced lead times
- Lower production costs
- Improved part quality
- Fewer manufacturing defects
Contact our injection molding design team now!
Key design reservations
Effective injection molding design includes several critical concerns to ensure the final section is manufactured, quality, and performance. The key aspects to pay attention to this are:
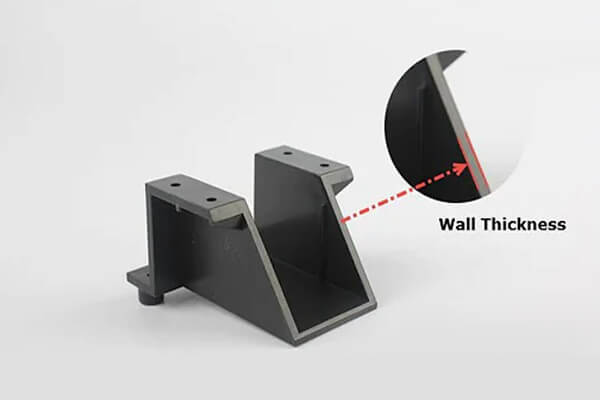

wall thickness design
Uniform wall thickness is the most important aspect of injection molding design. Variations in wall thickness can result in several issues, such as uneven cooling, sink marks, and warping. The thickness of the wall should be permanent to ensure its cooling and stability.
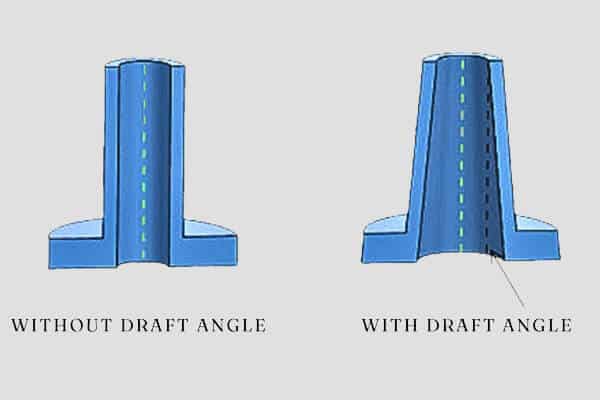
Draft angles design
The draft angle has minor tappers on the vertical levels of a part, usually from 1 to 3 degrees. It needs to easily exclude this section from the mold, reduce the risk of damage, and ensure high-quality parts.
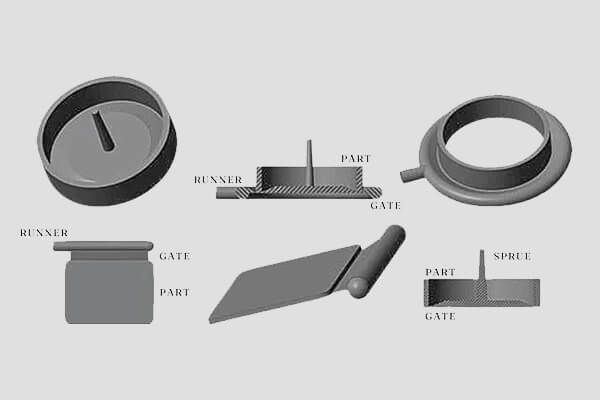
gate design
The correct gate design depends on the part size, geometry, and material. Proper placement and sizing are critical to efficient filling and quality.
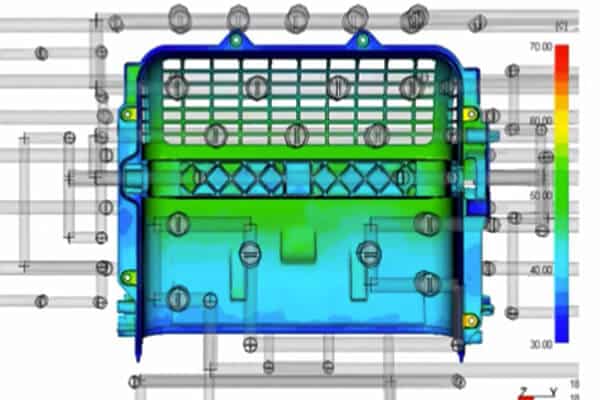
cooling system design
The design of the cooling system is critical to controlling the mold temperature. Efficient cooling reduces cycle times and ensures uniform cooling, which is essential to maintaining part quality and preventing defects such as warping and sink marks.
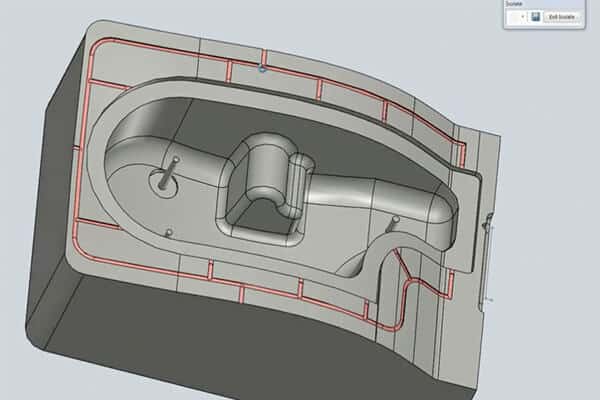
Venting system design
The primary function of mold slides is to enable the molding of parts with features that would otherwise lock them into the mold, preventing their ejection.
Normal challenges and solutions
Injection molding has many limitations that can compromise the final product's consistency and quality, even with its capacity and performance. Understanding these common problems and implementing practical solutions is crucial to improving the injection molding process.
Warping
Warping occurs when different areas of a part cool and shrink at different rates, causing a distorted form. It can be due to the uneven thickness of the wall, the cooling rates, or material properties.
Solution
- Uniform wall thickness: Make sure the part design maintains the permanent thickness of the wall to promote cooling.
- Material selection: Use the material with a low shrinking rate and stable thermal properties.
- Cooling system design: The mold cooling system should provide uniform cooling throughout the section. Conformal cooling channels should be used if necessary.
- Part geometry: Add ribs and gusts to increase structural integrity and reduce the chances of warping.
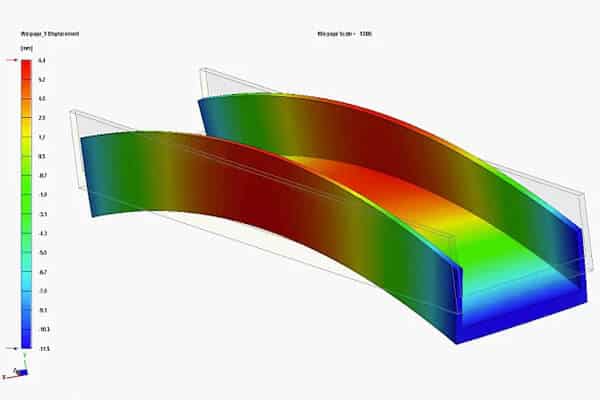
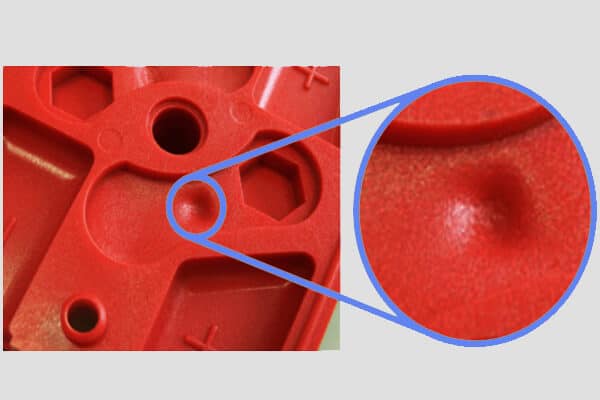
Sink marks
Due to local shrinking during cooling, sink Marks are depressed at the level of such a part. They often appear near obese parts or reinforce characteristics such as ribs and owners.
Solution
- Permanent wall thickness: Design parts with uniform thickness to minimize shrinking variation.
- Corrected rib and bass design: Ensure the ribs and owners are at most of the wall thickness.
- Packing pressure and time: Adjust the packing pressure and time to ensure proper compensation for shrinking.
- Cooling rate: Improve the cooling rate to ensure cooling reduces local shrinking chances.
Weld lines
Weld lines, or knitted lines, are found when two or more flow fronts do not completely bond, resulting in a weak suture. These lines are usually found around holes, inserting, or complex geometry.
Solution
- Gate location: Adjust the gate location to improve the flow style and minimize a multiple-flow front meeting.
- Injection speed and pressure: Increase the injection speed and pressure to ensure the bond fronts are more efficient.
- Use materials with good flow properties and those that are less likely to form a weld line.
- Mold temperature: Increase the mold temperature to enhance the ties of the flow fronts.
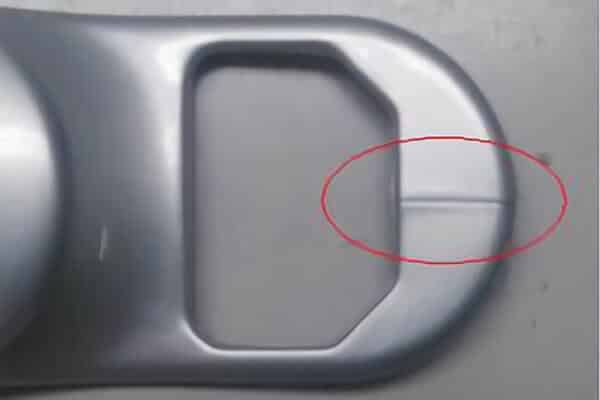

The traces of air and burning signs
Air nets are found when the air is trapped inside the mold, causing the video to be incomplete and filled. Burning marks due to high temperature are trapped in black spots on the surface of the portion.
Solution
- Ensure appropriate venting in the mold to allow the trapped air to escape. Appropriately sized and positioned vents are significant.
- Mold design: Edit the mold design to facilitate smooth flow and reduce the chances of rebuilding.
- Injection speed: Adjust the speed of the injection to prevent the formation of air nets and reduce the risk of burning scars.
- Vacuum molding: Consider using vacuum assistance molding to remove air from the mold's cavity before the injection.
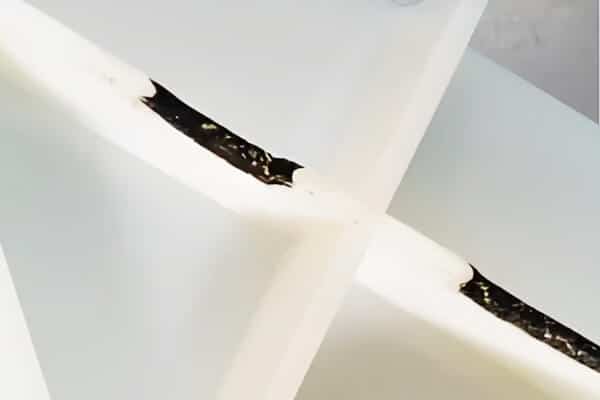

Flash
Flash is more plastic that exits the mold cavity and forms a thin layer on the edges of the part. This happens when half of the mold is not closed correctly, or the needle is under excessive pressure.
Solution
- Mold maintenance: Regularly maintain to ensure proper alignment and closure.
- Clamping force: Increase clamping to ensure the mold parts are safely shut down during injection.
- Injection pressure: Improve the pressure to force the extra material from the cavity.
- Parting line design: Design a separate line carefully to ensure a strict fit between mold parts.
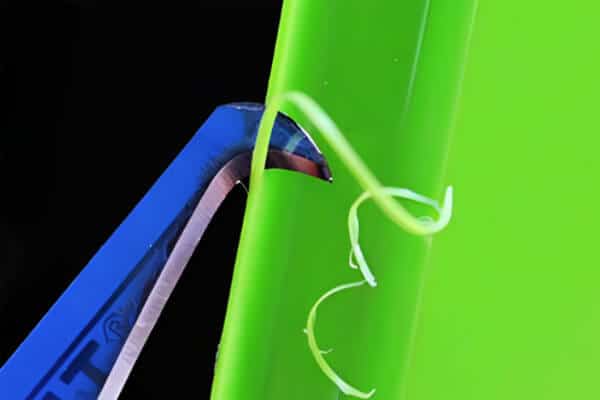

Short shots
When the mold cavity is not filled, short shots occur at a time, resulting in incomplete parts. This may be due to insufficient material, low injection pressure, or inadequate venting.
Solution
- Material volume: Make sure the exact amount of material is used for each injection cycle.
- Injection pressure and speed: Increase the injection pressure and speed to fill the mold cavity.
- Venting: Improve mold venting to escape the air and prevent short shots.
- Gate size and location: Improve the size and location of the gate to increase the material flow in the mold cavity.
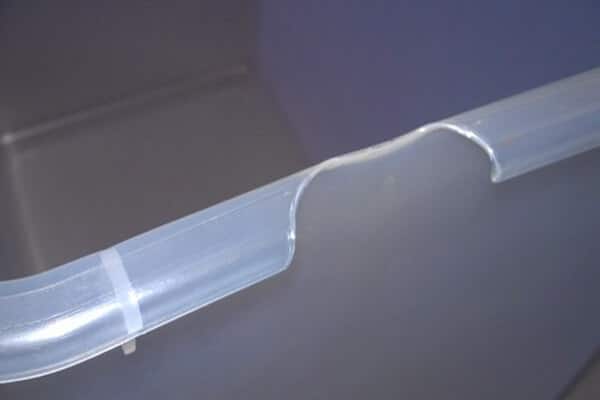

Bubbles and voids
Internal defects caused by air or gas trapped within the bubbles and voids section can weaken this section and affect its appearance and performance.
Solution
- Drying material: Make sure the material is properly dried before the injection to prevent moisture from causing bubbles.
- Venting: Improve venting to allow trapped air to escape during injection.
- Injection speed: Adjust the injection speed to reduce the chances of entering the air.
- Packing Pressure: Increase packing pressure to fill the voids and reduce the formation of bubbles.

Partner with YUCO for injection molding design solutions
As a leading Chinese injection molding design services provider, YUCO brings unparalleled expertise and innovation to every project. Our team of highly skilled engineers and designers draws on decades of combined experience to deliver exceptional results for clients across a variety of industries.
Standing at the forefront of industry advancements, YUCO continuously incorporates innovative technologies and methods into our design practices:
- Sustainability in injection molding design
- Advanced materials (biodegradable plastics, composites).
- Innovations in mold making (3D printed molds, advanced CNC)
- Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing.
Contact us today to elevate your injection molding projects with our expert design services.
Tel: +86 13586040750