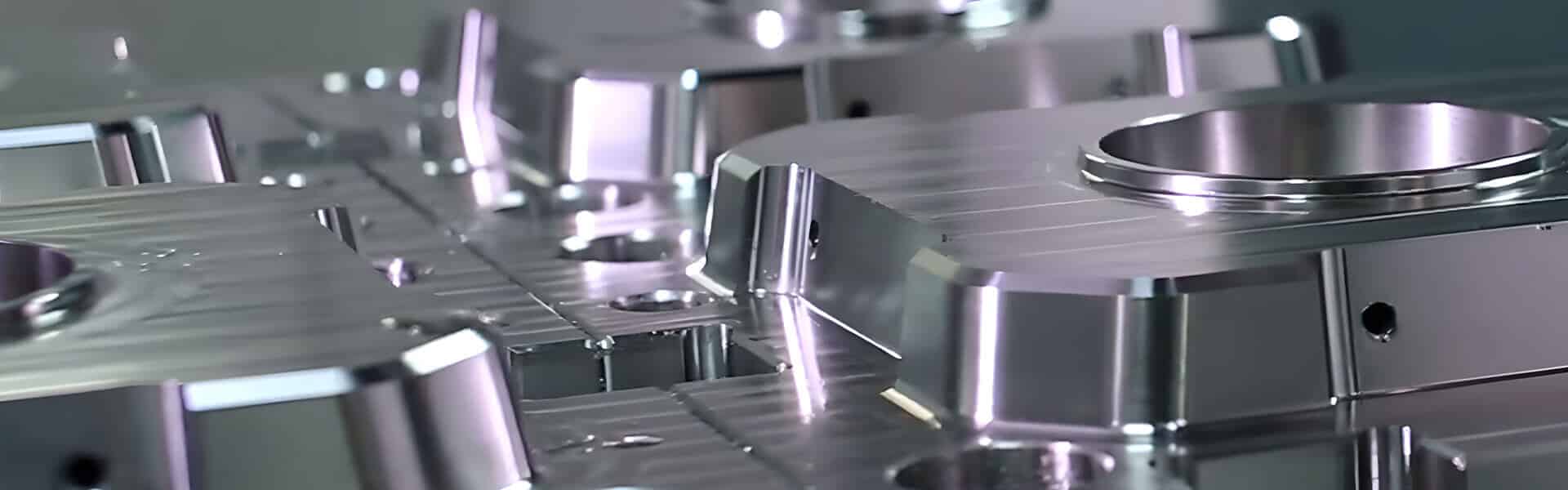
An injection mold is a specialized, high-precision tool used to form molten plastic into a desired shape. During the injection molding process, plastic material is melted, injected into the mold cavity, cooled, and then ejected as a finished product. The mold determines the product’s final appearance, accuracy, and strength, making it a key factor in overall product quality.
At YUCO Mold, a professional injection mold manufacturer in China, we understand that the efficiency, quality, and durability of molded products depend on each mold component. From the sprue to the subrunner and exhaust port, each element plays a critical role in the process.
Whether you’re learning about injection molding for the first time or starting your own production, this article explains the main components of an injection mold and how each part functions together to ensure smooth operation and reliable production performance.
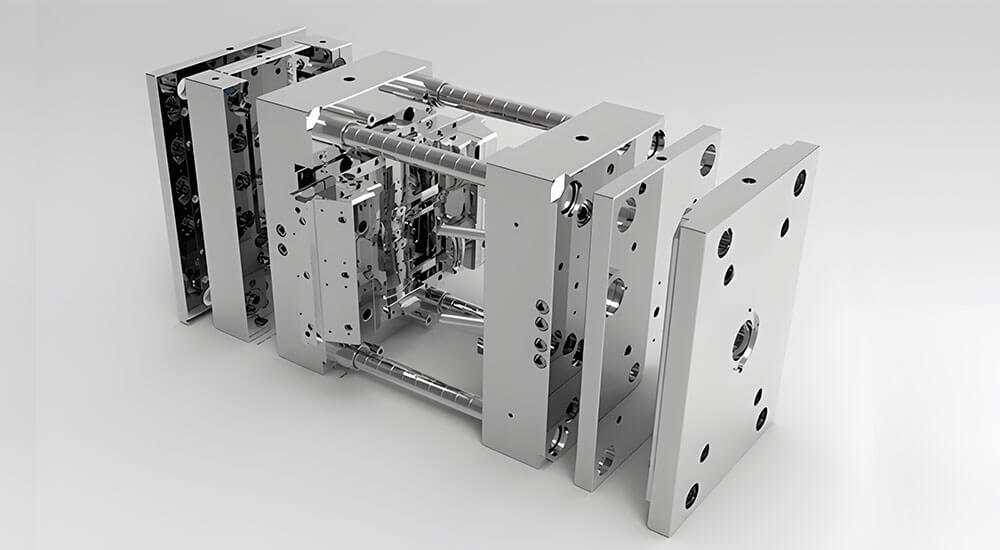
Key injection mold components
What determines the quality and properties of a plastic product in injection molding? The components of the injection mold play a crucial role in product quality, efficiency, design accuracy, finish, and overall performance. By selecting the right components when building the mold, you ensure that your product meets every requirement on the production checklist.
Below, we explore some of the essential components of an injection mold in detail:
The mold base (The foundation)
The mold base forms the framework of the mold assembly and serves as the primary structure that holds all other components together. Constructed from robust steel or aluminum alloy, it provides stability, alignment, and support to withstand the forces and stresses encountered during injection molding. A well-designed mold base ensures that each cycle produces parts with consistent precision and quality.
The mold base securely holds the cavity and core plates, featuring guide pin holes and alignment locks to maintain precise alignment and accurate parting line matching. It also includes ejector pin holes for proper, damage-free removal of finished parts and often incorporates cooling channels to facilitate uniform mold cooling and enhance part quality.
Main components and their roles
- Fixed and moving platens – Form the two main sides of the mold. The fixed platen attaches to the injection molding machine, while the moving platen enables the mold to open and close during each cycle.
- Support blocks – Strengthen the mold base and distribute injection pressure evenly to prevent deformation.
- Cavity and core plates – Form the shape of the molded part. The cavity plate creates the external surface, and the core plate forms the internal shape.
- Guide pins – Ensure perfect alignment between cavity and core sides, allowing smooth and precise mold closing without misalignment or damage.
Materials used
Common materials include high-quality steel and aluminum. Steel offers durability, wear resistance, and the ability to withstand high injection pressures, making it ideal for mass production. Aluminum is lightweight with excellent heat conductivity, reducing cooling time and making it suitable for prototypes or short-run molds.
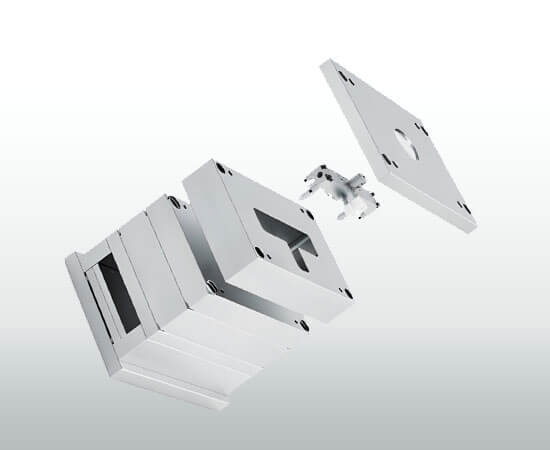

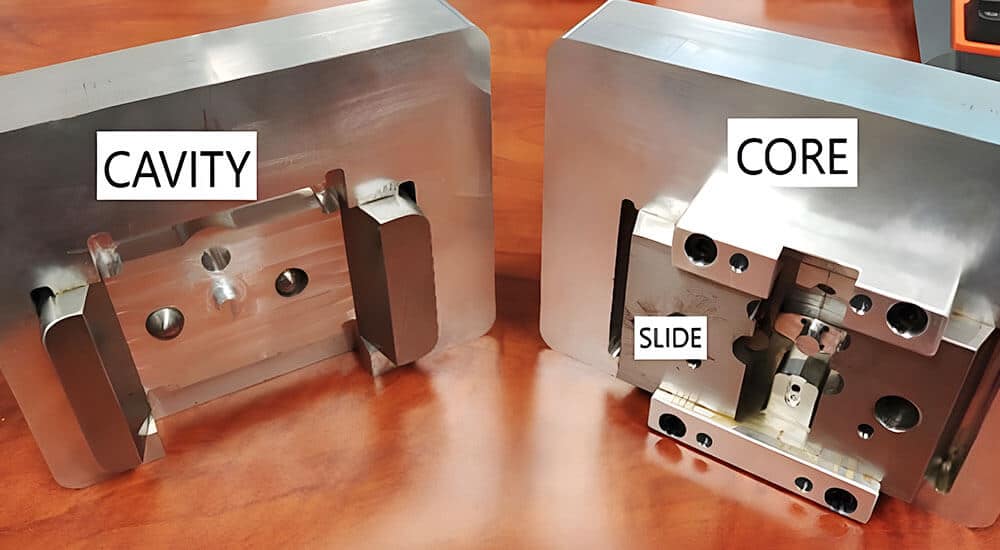
The cavity and core (The part-forming features)
The cavity and core are the heart of an injection mold, forming the actual shape of the finished plastic product. Molten plastic injected into the mold fills the space between the cavity and core, solidifies, and takes on the desired form. The precision and surface quality of these components directly affect the product’s accuracy, texture, and strength.
Difference between the core and cavity
- Cavity (A-side): Forms the outer surface of the molded part. It is usually mounted on the fixed side of the mold and remains stationary during the process.
- Core (B-side): Shapes the inner surface or features of the part. It is attached to the moving side of the mold and is responsible for ejecting the part once it cools.
Together, the cavity and core define the product’s external and internal geometry, ensuring the final piece meets design specifications.
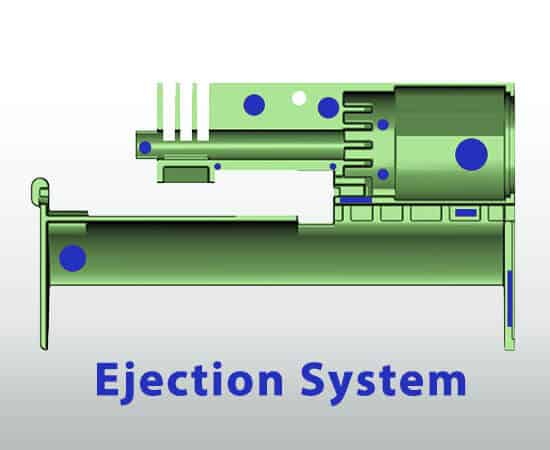
The ejection system (The release mechanism)
The ejection system, or release mechanism, ensures the molded product is safely and efficiently removed after cooling and solidifying. Once the mold opens, the system pushes the finished part out of the cavity, allowing the next molding cycle to begin. A properly designed ejection system prevents part damage, deformation, or surface marks, maintaining product quality and consistent production flow.
Main components
- Ejector pins: Small, precisely positioned pins that push the molded part out of the core when the mold opens. Usually cylindrical with a rounded or flat end, they are made of hardened steel to withstand extraction forces. Their size, number, and placement depend on mold design, part geometry, and injection requirements. Regular inspection and lubrication prevent sticking or binding and maintain smooth operation.
- Ejector plates: Hold and control multiple ejector pins. When the mold opens, the plates move forward, activating the pins simultaneously to release the part evenly.
- Return pins: Guide the ejector plates and pins back to their original positions after ejection, preparing the mold for the next cycle.
Other ejection methods
- Sleeve ejectors: Used for cylindrical or hollow parts, such as tubes or caps, where the ejector surrounds the core for uniform release.
- Blade ejectors: Thin, flat components for parts with narrow or sharp-edged surfaces that standard pins cannot reach.
- Stripper plates: Push the part out evenly across its entire surface, ideal for large or flat products requiring gentle, uniform ejection to prevent warping or scratches.
Cooling system
The cooling system regulates the mold’s temperature during injection molding, ensuring molten plastic cools and solidifies at the proper rate. The cooling system removes heat evenly by circulating a fluid—usually water or oil—through channels within the mold. Proper temperature control improves part accuracy and surface quality while shortening cycle times, increasing production efficiency without compromising quality.
Main components
- Cooling channels: Precision-drilled passages inside the mold base and plates that allow coolant to flow near cavity and core surfaces. Their design and placement determine the efficiency and uniformity of mold cooling.
- Baffles: Thin plates inserted into the channels to redirect coolant, distributing it across wider areas for even temperature control, particularly in large or flat molds.
- Bubblers: Used for deep or narrow mold sections where straight channels are difficult to drill. They guide coolant through confined spaces, improving circulation in hard-to-reach areas.
The runner system (The delivery)
The runner system, or delivery system, guides molten plastic from the injection molding machine’s nozzle to the mold cavity. Acting as a network of channels, it controls the flow, temperature, and pressure of the molten material, ensuring the mold fills evenly and efficiently.
The material’s viscosity, molding parameters, and part geometry affect runners’ size, shape, and quantity. A well-designed runner system prevents defects such as short shots, air traps, or uneven filling, which can affect part quality and appearance.
Main parts of the runner system
- Sprue: The main entry point for molten plastic, connecting the machine nozzle to the runner system and directing material into the mold.
- Runners: Horizontal channels branching from the sprue that distribute molten plastic to multiple cavities. Their size, length, and shape are carefully designed to maintain balanced flow and consistent pressure.
- Gate: The final opening connecting the runner to the mold cavity. It controls flow rate, influences surface quality, and affects part removal. Proper gate design ensures high-quality parts and minimizes potential defects.
Hot runner system (Optional upgrade)
The hot runner system eliminates the need for traditional sprues and runners. Using a heated manifold and nozzles, molten plastic is injected directly into the cavities while maintaining temperature. This system reduces material waste, shortens cycle times, and produces parts with consistent quality and better surface finishes. Hot runners are ideal for high-volume production and require proper maintenance to operate efficiently.
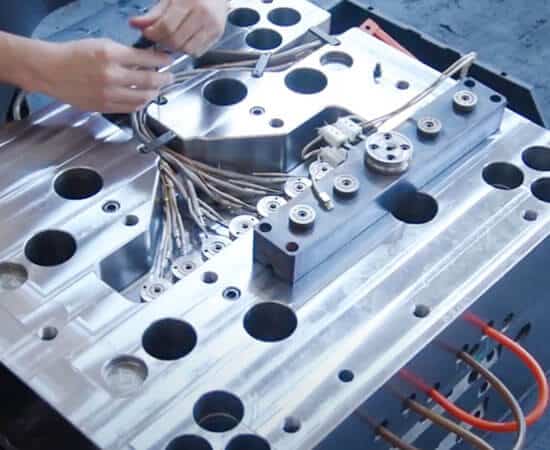

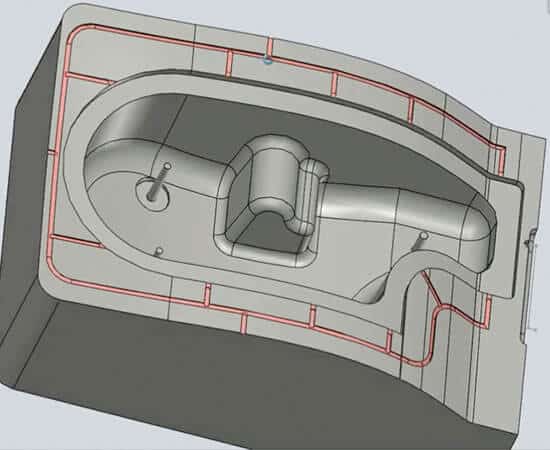
The venting system (Air release)
The venting system, or air release system, allows trapped air and gases to escape from the mold cavity during injection. It is essential in injection molds to ensure proper air and gas evacuation, improve material flow, remove volatiles, and protect mold integrity.
Without proper venting, trapped air can cause defects such as burn marks, short shots, or poor surface finishes. Burn marks occur when compressed air overheats, and short shots happen when air blocks the cavity, preventing full plastic flow. Poor venting may also create visible flow lines or weak spots in the final product.
Vents are small, shallow grooves located along parting lines, ejector pin areas, or slides of mold. They are machined to allow air to escape while preventing plastic leakage. Some molds use micro-vents or vacuum-assisted systems to remove air more efficiently, especially in complex designs.
Routine maintenance, including cleaning and inspection, ensures proper venting, helping achieve defect-free parts, maintain quality, and prolong mold life.
The clamping system (Mold alignment and support)
The clamping system keeps the mold halves securely closed and perfectly aligned during the injection process. When molten plastic is injected under high pressure, the mold must remain tightly sealed to prevent material leakage and maintain part accuracy. The clamping system provides the force and structural support needed to ensure each molding cycle runs smoothly and safely.
A precise clamping system prevents leaks, deformation, and misalignment, ensuring consistent part dimensions and surface finish. Proper alignment also reduces wear on other mold components, extending mold life. By ensuring stable alignment and secure closure, YUCO Mold delivers molds that consistently produce accurate, durable, and visually flawless plastic parts.
Main components
- Clamping plates: Attach the mold to the injection molding machine’s platens. The fixed clamping plate holds the stationary half of the mold, while the moving clamping plate supports the half that opens and closes during each cycle. Together, they maintain stability and proper positioning.
- Alignment features: Guide pins, bushings, and interlocks ensure the mold halves align perfectly every time. Guide pins slide into bushings to form a mechanism that guarantees consistent parting line matching, precise alignment, and reduced binding or friction. Regular inspection and maintenance prevent wear and maintain high-quality output.
Optional and specialized components
Optional and specialized components are typically added to complex or multi-part molds where standard components cannot achieve the desired shape or function. They are designed to handle complex shapes, multi-part products, or unique production requirements. These components enhance the mold’s functionality, efficiency, and flexibility, enabling the production of parts that would be difficult or impossible with a basic mold design.
- Slides: Move horizontally within the mold to form side holes or features that cannot be created by simple mold opening and closing. They automatically retract when the mold opens and are essential for producing parts with intricate geometries, such as side holes or undercuts. Slides are usually made of hardened steel and require proper alignment, maintenance, and lubrication to ensure smooth operation.
- Lifters: Move at an angle during ejection to release parts with undercuts or other features that prevent straight ejection, ensuring smooth part removal and maintaining quality.
- Inserts: Removable components placed in the cavity or core to form fine details or simplify maintenance. They allow customization or replacement without changing the entire mold.
- Core pulls: Mechanisms used to create internal holes, threads, or side openings. They move in and out of the mold to form these features and retract before ejection to prevent part damage.
By integrating these features, manufacturers can produce intricate products with tighter tolerances and smoother finishes.
Conclusion
Every component of an injection mold from the mold base that provides structure and alignment, to the runner system that delivers molten plastic, the cavity and core that shape the part, and the ejection and cooling systems that ensure smooth release and stable temperature plays a vital role in producing high-quality, consistent molded parts. Together, these systems form an interconnected process where precision, balance, and timing are critical to every successful molding cycle.
With knowledge of how these components interact, YUCO can produce plastics that meet the highest standards. As a professional injection mold manufacturer in China, YUCO Mold is committed to delivering molds that combine precision engineering, reliable performance, and long-lasting durability.
For improved molding efficiency or custom mold solutions, contact YUCO Mold today and let our expertise help you achieve outstanding production results.
